Mechanical hypersensitivity, sympathetic sprouting, and glial activation are attenuated by local injection of corticosteroid near the lumbar ganglion in a rat model of neuropathic pain
- PMID: 21455091
- PMCID: PMC3076946
- DOI: 10.1097/AAP.0b013e318203087f
Mechanical hypersensitivity, sympathetic sprouting, and glial activation are attenuated by local injection of corticosteroid near the lumbar ganglion in a rat model of neuropathic pain
Abstract
Background and objectives: Inflammatory responses in the lumbar dorsal root ganglion (DRG) play a key role in pathologic pain states. Systemic administration of a common anti-inflammatory corticosteroid, triamcinolone acetonide (TA), reduces sympathetic sprouting, mechanical pain behavior, spontaneous bursting activity, and cytokine and nerve growth factor production in the DRG. We hypothesized that systemic TA effects are primarily due to local effects on the DRG.
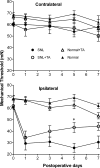
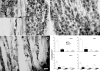
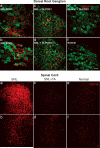
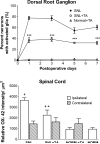
Methods: Male Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into 4 groups: SNL (tight ligation and transection of spinal nerves) and normal with and without a single dose of TA injectable suspension slowly injected onto the surface of DRG and surrounding region at the time of SNL or sham surgery. Mechanical threshold was tested on postoperative days 1, 3, 5, and 7. Immunohistochemical staining examined tyrosine hydroxylase and glial fibrillary acidic protein in DRG and CD11B antibody (OX-42) in spinal cord.
Results: Local TA treatment attenuated mechanical sensitivity, reduced sympathetic sprouting in the DRG, and decreased satellite glia activation in the DRG and microglia activation in the spinal cord after SNL.
Conclusions: A single injection of corticosteroid in the vicinity of the axotomized DRG can mimic many effects of systemic TA, mitigating behavioral and cellular abnormalities induced by spinal nerve ligation. This provides a further rationale for the use of localized steroid injections clinically and provides further support for the idea that localized inflammation at the level of the DRG is an important component of the spinal nerve ligation model, commonly classified as neuropathic pain model.
Figures
References
-
- Moalem G, Tracey DJ. Immune and inflammatory mechanisms in neuropathic pain. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2006;51:240–64. - PubMed
-
- DeLeo JA, Tanga FY, Tawfik VL. Neuroimmune activation and neuroinflammation in chronic pain and opioid tolerance/hyperalgesia. Neuroscientist. 2004;10:40–52. - PubMed
-
- Hanani M. Satellite glial cells in sensory ganglia: from form to function. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2005;48:457–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
