Protective effect of bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus) against doxorubicin-induced oxidative cardiotoxicity in rats
- PMID: 21455099
- PMCID: PMC3539517
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.881711
Protective effect of bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus) against doxorubicin-induced oxidative cardiotoxicity in rats
Abstract
Background: Doxorubicin (DOX) is a commonly used chemotherapeutic agent. It is associated with serious dose-limiting cardiotoxicity, which is at least partly caused by generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Supplementations with bilberries were effective in reducing oxidative stress in many tissue injuries due their high content of antioxidants. The present study investigated the potential protective effect of bilberry extract against DOX-induced cardiotoxicity in rats.
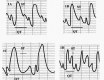
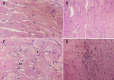
Material/methods: Rats were treated orally with a methanolic extract of bilberry for 10 days. DOX was injected intraperitoneally on day 7. Twenty-four hours after the last bilberry administration, rats were subjected to ECG study. Blood was then withdrawn and cardiac tissues were dissected for assessment of oxidative stress and cardiac tissue injury. Cardiac tissues were also subjected to histopathological examination.
Results: Bilberry extract significantly inhibited DOX-provoked reduced glutathione depletion and accumulation of oxidized glutathione, malondialdehyde and protein carbonyls in cardiac tissues. This was accompanied by significant amelioration of reduced cardiac catalase, superoxide dismutase, and glutathione peroxidase activities; and increased cardiac myeloperoxidase activity in response to DOX challenge. Pretreatment with bilberry significantly guarded against DOX-induced increase in serum activities of lactate dehydrogenase, creatine phosphokinase and creatine kinase-MB, as well as the level of troponin I. Bilberry alleviated ECG changes in rats treated with DOX and attenuated its pathological changes.
Conclusions: Bilberry protects against DOX-induced cardiotoxicity in rats. This can be attributed, at least in part, to its antioxidant activity.
Figures

References
-
- Shan K, Lincoff AM, Young JB. Anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity. Ann Intern Med. 1996;125:47–58. - PubMed
-
- Hortobagyi GN. Anthracyclines in the treatment of cancer. An overview. Drugs. 1997;54:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Myers C, Bonow R, Palmeri S, et al. A randomized controlled trial assessing the prevention of doxorubicin cardiomyopathy by N-acetylcysteine. Semin Oncol. 1983;10:53–55. - PubMed
-
- Singal PK, Segstro RJ, Singh RP, Kutryk MJ. Changes in lysosomal morphology and enzyme activities during the development of adriamycin-induced cardiomyopathy. Can J Cardiol. 1985;1:139–47. - PubMed
-
- Singal PK, Deally CM, Weinberg LE. Subcellular effects of adriamycin in the heart: a concise review. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1987;19:817–28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

