Access to biologic treatment for rheumatoid arthritis in Central and Eastern European (CEE) countries
- PMID: 21455121
- PMCID: PMC3539513
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.881697
Access to biologic treatment for rheumatoid arthritis in Central and Eastern European (CEE) countries
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to assess and compare patients' access to biologic anti-RA drugs in selected Central and Eastern European (CEE) countries and to analyze the determinants of differences between countries.
Material/methods: This is a multi-country survey study, based on a combination of desk research and direct contact with national RA stakeholders. Data was collected using a pre-defined questionnaire. Affordability was measured using an affordability index, calculated comparing the index of health care expenditures to the price index, using Poland as an index of 1.
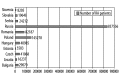
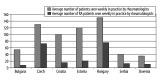
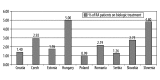
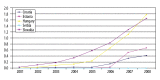
Results: The percentage of patients on biologic treatment in 2009 was highest in Hungary (5% RA patients on biologic treatment), followed by Slovenia (4.5%), Slovakia (3.5%), Czech Republic (2.92%), Romania (2.2%), Estonia (1.8%), and Croatia, Serbia, Poland (below 1.5%). Infliximab, etanercept, adalimumab and rituximab were included in the reimbursement system in all countries, but abatacept and tocilizumab were included only in Slovakia. In Slovenia, public payer covered 75% of the price, and 25% is covered by supplementary health insurance; in Bulgaria public payer covered 50% of etanercept and adalimumab costs, and 75% of rituximab cost. In other countries, biologic drugs are reimbursed at 100%. Affordability index for biologic drugs was the lowest in Slovenia (0.4). In each country national guidelines define which patients are eligible for biologic treatment. Disease Activity Score (DAS28) of over 5.1 and failure of 2 or more disease-modifying anti-RA drugs, including methotrexate, are commonly used criteria.
Conclusions: The most important factors limiting access to biologic anti-RA treatment in the CEE region are macroeconomic conditions and restrictive treatment guidelines.
Figures


References
-
- Hanova P, Pavelka K, Dostal C, et al. Epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile idiopathic arthritis and gout in two regions of the Czech Republic in a descriptive population-based survey in 2002–2003. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2006;24(4):499–507. - PubMed
-
- Otsa K, Tammaru M, Vorobjov S, et al. The prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in Harju County, Estonia. EULAR. 2009 Abstract FRI0517. - PubMed
-
- Kiss CG, Lovei C, Suto G, et al. Prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in the South-Transdanubian region of Hungary based on a representative survey of 10,000 inhabitants. J Rheumatol. 2005;32(9):1688–90. - PubMed
-
- Péntek M, Kobelt G, Czirják L, et al. Costs of rheumatoid arthritis in Hungary. J Rheumatol. 2007;34(6):1437–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

