CRISPR RNA maturation by trans-encoded small RNA and host factor RNase III
- PMID: 21455174
- PMCID: PMC3070239
- DOI: 10.1038/nature09886
CRISPR RNA maturation by trans-encoded small RNA and host factor RNase III
Abstract
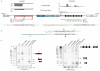
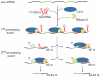
CRISPR/Cas systems constitute a widespread class of immunity systems that protect bacteria and archaea against phages and plasmids, and commonly use repeat/spacer-derived short crRNAs to silence foreign nucleic acids in a sequence-specific manner. Although the maturation of crRNAs represents a key event in CRISPR activation, the responsible endoribonucleases (CasE, Cas6, Csy4) are missing in many CRISPR/Cas subtypes. Here, differential RNA sequencing of the human pathogen Streptococcus pyogenes uncovered tracrRNA, a trans-encoded small RNA with 24-nucleotide complementarity to the repeat regions of crRNA precursor transcripts. We show that tracrRNA directs the maturation of crRNAs by the activities of the widely conserved endogenous RNase III and the CRISPR-associated Csn1 protein; all these components are essential to protect S. pyogenes against prophage-derived DNA. Our study reveals a novel pathway of small guide RNA maturation and the first example of a host factor (RNase III) required for bacterial RNA-mediated immunity against invaders.
Figures
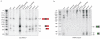

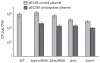
Comment in
-
Microbiology: Dicing defence in bacteria.Nature. 2011 Mar 31;471(7340):588-9. doi: 10.1038/471588a. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21455171 No abstract available.
References
-
- Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T. Molecular Cloning: a Laboratory Manual. 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; Cold Spring Harbor, N. Y.: 1989. edn.
-
- Caparon MG, Scott JR. Genetic manipulation of pathogenic streptococci. Methods Enzymol. 1991;204:556–586. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

