SHARPIN forms a linear ubiquitin ligase complex regulating NF-κB activity and apoptosis
- PMID: 21455181
- PMCID: PMC3085511
- DOI: 10.1038/nature09814
SHARPIN forms a linear ubiquitin ligase complex regulating NF-κB activity and apoptosis
Abstract
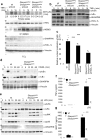
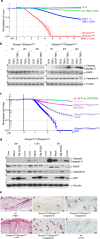
SHARPIN is a ubiquitin-binding and ubiquitin-like-domain-containing protein which, when mutated in mice, results in immune system disorders and multi-organ inflammation. Here we report that SHARPIN functions as a novel component of the linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex (LUBAC) and that the absence of SHARPIN causes dysregulation of NF-κB and apoptotic signalling pathways, explaining the severe phenotypes displayed by chronic proliferative dermatitis (cpdm) in SHARPIN-deficient mice. Upon binding to the LUBAC subunit HOIP (also known as RNF31), SHARPIN stimulates the formation of linear ubiquitin chains in vitro and in vivo. Coexpression of SHARPIN and HOIP promotes linear ubiquitination of NEMO (also known as IKBKG), an adaptor of the IκB kinases (IKKs) and subsequent activation of NF-κB signalling, whereas SHARPIN deficiency in mice causes an impaired activation of the IKK complex and NF-κB in B cells, macrophages and mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs). This effect is further enhanced upon concurrent downregulation of HOIL-1L (also known as RBCK1), another HOIP-binding component of LUBAC. In addition, SHARPIN deficiency leads to rapid cell death upon tumour-necrosis factor α (TNF-α) stimulation via FADD- and caspase-8-dependent pathways. SHARPIN thus activates NF-κB and inhibits apoptosis via distinct pathways in vivo.
Figures


References
-
- Grabbe C, Dikic I. Functional roles of ubiquitin-like domain (ULD) and ubiquitin-binding domain (UBD) containing proteins. Chem Rev. 2009;109(4):1481–1494. - PubMed
-
- Seymour RE, et al. Spontaneous mutations in the mouse Sharpin gene result in multiorgan inflammation, immune system dysregulation and dermatitis. Genes Immun. 2007;8(5):416–421. - PubMed
-
- Hayden MS, Ghosh S. Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell. 2008;132(3):344–362. - PubMed
-
- Wertz IE, Dixit VM. Ubiquitin-mediated regulation of TNFR1 signaling. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2008;19(3–4):313–324. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

