Evaluating gene expression in C57BL/6J and DBA/2J mouse striatum using RNA-Seq and microarrays
- PMID: 21455293
- PMCID: PMC3063777
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017820
Evaluating gene expression in C57BL/6J and DBA/2J mouse striatum using RNA-Seq and microarrays
Abstract
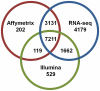
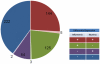
C57BL/6J (B6) and DBA/2J (D2) are two of the most commonly used inbred mouse strains in neuroscience research. However, the only currently available mouse genome is based entirely on the B6 strain sequence. Subsequently, oligonucleotide microarray probes are based solely on this B6 reference sequence, making their application for gene expression profiling comparisons across mouse strains dubious due to their allelic sequence differences, including single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). The emergence of next-generation sequencing (NGS) and the RNA-Seq application provides a clear alternative to oligonucleotide arrays for detecting differential gene expression without the problems inherent to hybridization-based technologies. Using RNA-Seq, an average of 22 million short sequencing reads were generated per sample for 21 samples (10 B6 and 11 D2), and these reads were aligned to the mouse reference genome, allowing 16,183 Ensembl genes to be queried in striatum for both strains. To determine differential expression, 'digital mRNA counting' is applied based on reads that map to exons. The current study compares RNA-Seq (Illumina GA IIx) with two microarray platforms (Illumina MouseRef-8 v2.0 and Affymetrix MOE 430 2.0) to detect differential striatal gene expression between the B6 and D2 inbred mouse strains. We show that by using stringent data processing requirements differential expression as determined by RNA-Seq is concordant with both the Affymetrix and Illumina platforms in more instances than it is concordant with only a single platform, and that instances of discordance with respect to direction of fold change were rare. Finally, we show that additional information is gained from RNA-Seq compared to hybridization-based techniques as RNA-Seq detects more genes than either microarray platform. The majority of genes differentially expressed in RNA-Seq were only detected as present in RNA-Seq, which is important for studies with smaller effect sizes where the sensitivity of hybridization-based techniques could bias interpretation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Hitzemann R, Malmanger B, Reed C, Lawler M, Hitzemann B, et al. A strategy for the integration of QTL, gene expression, and sequence analyses. Mamm Genome. 2003;14:733–747. - PubMed
-
- Wang H, Zhu YZ, Wong PT, Farook JM, Teo AL, et al. cDNA microarray analysis of gene expression in anxious PVG and SD rats after cat-freezing test. Exp Brain Res. 2003;149:413–421. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- AA011114/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA011114/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA005228/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AA010760/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- AA013484/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AA007468/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- T32AA07468/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- 5T15LM007088/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- R29 AA011114/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- 5P30CA069533-13/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA013484/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- T32DA07262/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024140/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AA010760/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- MH051372/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DA007262/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA011034/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- AA011034/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH051372/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T15 LM007088/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- DA005228/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AA010760/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA069533/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5UL1RR024140/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

