Colocalization of hyperpolarization-activated, cyclic nucleotide-gated channel subunits in rat retinal ganglion cells
- PMID: 21456027
- PMCID: PMC3287082
- DOI: 10.1002/cne.22638
Colocalization of hyperpolarization-activated, cyclic nucleotide-gated channel subunits in rat retinal ganglion cells
Abstract
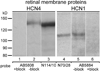
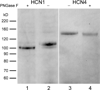
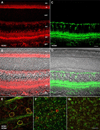
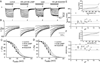
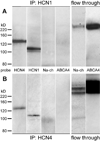
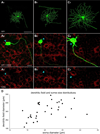
The current-passing pore of mammalian hyperpolarization-activated, cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channels is formed by subunit isoforms denoted HCN1-4. In various brain areas, antibodies directed against multiple isoforms bind to single neurons, and the current (I(h)) passed during hyperpolarizations differs from that of heterologously expressed homomeric channels. By contrast, retinal rod, cone, and bipolar cells appear to use homomeric HCN channels. Here, we assess the generality of this pattern by examining HCN1 and HCN4 immunoreactivity in rat retinal ganglion cells, measuring I(h) in dissociated cells, and testing whether HCN1 and HCN4 proteins coimmunoprecipitate. Nearly half of the ganglion cells in whole-mounted retinae bound antibodies against both isoforms. Consistent with colocalization and physical association, 8-bromo-cAMP shifted the voltage sensitivity of I(h) less than that of HCN4 channels and more than that of HCN1 channels, and HCN1 coimmunoprecipitated with HCN4 from membrane fraction proteins. Finally, the immunopositive somata ranged in diameter from the smallest to the largest in rat retina, the dendrites of immunopositive cells arborized at various levels of the inner plexiform layer and over fields of different diameters, and I(h) activated with similar kinetics and proportions of fast and slow components in small, medium, and large somata. These results show that different HCN subunits colocalize in single retinal ganglion cells, identify a subunit that can reconcile native I(h) properties with the previously reported presence of HCN4 in these cells, and indicate that I(h) is biophysically similar in morphologically diverse retinal ganglion cells and differs from I(h) in rods, cones, and bipolar cells.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures





References
-
- Abbas SY, Ying SW, Goldstein PA. Compartmental distribution of hyperpolarization-activated cyclic-nucleotide-gated channel 2 and hyperpolarization-activated cyclic-nucleotide-gated channel 4 in thalamic reticular and thalamocortical relay neurons. Neurosci. 2006;141:1811–1825. - PubMed
-
- Bhongsatiern J, Ohtsuki S, Tachikawa M, Hori S, Terasaki T. Retinal-specific ATP-binding cassette transporter (ABCR/ABCA4) is expressed at the choroid plexus in rat brain. J Neurochem. 2005;92:1277–1280. - PubMed
-
- Biel M, Michalakis S. Cyclic nucleotide-gated channels. Handb Exp Pharm. 2009;191:111–136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

