A high-resolution linkage map for comparative genome analysis and QTL fine mapping in Asian seabass, Lates calcarifer
- PMID: 21457569
- PMCID: PMC3088568
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-174
A high-resolution linkage map for comparative genome analysis and QTL fine mapping in Asian seabass, Lates calcarifer
Abstract
Background: High density linkage maps are essential for comparative analysis of synteny, fine mapping of quantitative trait loci (QTL), searching for candidate genes and facilitating genome sequence assembly. However, in most foodfish species, marker density is still low. We previously reported a first generation linkage map with 240 DNA markers and its application to preliminarily map QTL for growth traits in Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer). Here, we report a high-resolution linkage map with 790 microsatellites and SNPs, comparative analysis of synteny, fine-mapping of QTL and the identification of potential candidate genes for growth traits.
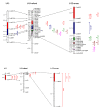
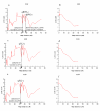
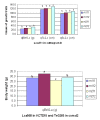
Results: A second generation linkage map of Asian seabass was developed with 790 microsatellite and SNP markers. The map spanned a genetic length of 2411.5 cM, with an average intermarker distance of 3.4 cM or 1.1 Mb. This high density map allowed for comparison of the map with Tetraodon nigroviridis genome, which revealed 16 synteny regions between the two species. Moreover, by employing this map we refined QTL to regions of 1.4 and 0.2 cM (or 400 and 50 kb) in linkage groups 2 and 3 in a population containing 380 progeny; potential candidate genes for growth traits in QTL regions were further identified using comparative genome analysis, whose effects on growth traits were investigated. Interestingly, a QTL cluster at Lca371 underlying growth traits of Asian seabass showed similarity to the cathepsin D gene of human, which is related to cancer and Alzheimer's disease.
Conclusions: We constructed a high resolution linkage map, carried out comparative mapping, refined the positions of QTL, identified candidate genes for growth traits and analyzed their effects on growth. Our study developed a framework that will be indispensable for further identification of genes and analysis of molecular variation within the refined QTL to enhance understanding of the molecular basis of growth and speed up genetic improvement of growth performance, and it also provides critical resource for future genome sequence assembly and comparative genomics studies on the evolution of fish genomes.
Figures

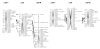


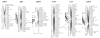
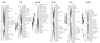



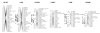
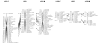



References
-
- Falconer DS, Mackay TFC. Introduction to Quantitative Genetics. Fourth. Harlow, Essex, UK: Addison Wesley Longman; 1996.
-
- Varshney RK, Tuberosa R, (eds) Genomics-Assisted Crop Improvement- Vol 2: Genomics Applications in Crops. Netherlands: Springer; 2007.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

