Ara h 1-reactive T cells in individuals with peanut allergy
- PMID: 21459424
- PMCID: PMC3130623
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2011.02.028
Ara h 1-reactive T cells in individuals with peanut allergy
Abstract
Background: Effective immunotherapy for peanut allergy is hampered by a lack of understanding of peanut-reactive CD4(+) T cells.
Objective: To identify, characterize, and track Ara h 1-reactive cells in subjects with peanut allergy by using Ara h 1-specific class II tetramers.
Methods: Tetramer-guided epitope mapping was used to identify the antigenic peptides within the peanut allergen Ara h 1. Subsequently, HLA class II/Ara h 1-specific tetramers were used to determine the frequency and phenotype of Ara h 1-reactive T cells in subjects with peanut allergy. Cytokine profiles of Ara h 1-reactive T cells were also determined.
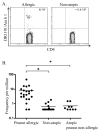
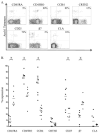
Results: Multiple Ara h 1 epitopes with defined HLA restriction were identified. Ara h 1-specific CD4(+) T cells were detected in all of the subjects with peanut allergy tested. Ara h 1-reactive T cells in subjects with allergy expressed CCR4 but did not express CRTH2. The percentage of Ara h1-reactive cells that expressed the β7 integrin was low compared with total CD4(+) T cells. Ara h 1- reactive cells that secreted IFN-γ, IL-4, IL-5, IL-10, and IL-17 were detected.
Conclusion: In individuals with peanut allergy, Ara h 1-reactive T cells occurred at moderate frequencies, were predominantly CCR4(+) memory cells, and produced IL-4. Class II tetramers can be readily used to detect Ara h 1-reactive T cells in the peripheral blood of subjects with peanut allergy without in vitro expansion and would be effective for tracking peanut-reactive CD4(+) T cells during immunotherapy.
Copyright © 2011 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. Published by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Sicherer SH, Munoz-Furlong A, Sampson HA. Prevalence of peanut and tree nut allergy in the United States determined by means of a random digit dial telephone survey: a 5-year follow-up study. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003;112(6):1203–7. - PubMed
-
- Oppenheimer JJ, Nelson HS, Bock SA, Christensen F, Leung DY. Treatment of peanut allergy with rush immunotherapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1992;90(2):256–62. - PubMed
-
- Nelson HS, Lahr J, Rule R, Bock A, Leung D. Treatment of anaphylactic sensitivity to peanuts by immunotherapy with injections of aqueous peanut extract. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997;99(6 Pt 1):744–51. - PubMed
-
- Bock SA, Munoz-Furlong A, Sampson HA. Further fatalities caused by anaphylactic reactions to food, 2001–2006. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;119(4):1016–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

