Whole genome siRNA cell-based screen links mitochondria to Akt signaling network through uncoupling of electron transport chain
- PMID: 21460183
- PMCID: PMC3093329
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E10-10-0854
Whole genome siRNA cell-based screen links mitochondria to Akt signaling network through uncoupling of electron transport chain
Abstract
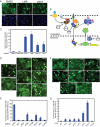
Forkhead transcription factors (FOXOs) alter a diverse array of cellular processes including the cell cycle, oxidative stress resistance, and aging. Insulin/Akt activation directs phosphorylation and cytoplasmic sequestration of FOXO away from its target genes and serves as an endpoint of a complex signaling network. Using a human genome small interfering RNA (siRNA) library in a cell-based assay, we identified an extensive network of proteins involved in nuclear export, focal adhesion, and mitochondrial respiration not previously implicated in FOXO localization. Furthermore, a detailed examination of mitochondrial factors revealed that loss of uncoupling protein 5 (UCP5) modifies the energy balance and increases free radicals through up-regulation of uncoupling protein 3 (UCP3). The increased superoxide content induces c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 (JNK1) kinase activity, which in turn affects FOXO localization through a compensatory dephosphorylation of Akt. The resulting nuclear FOXO increases expression of target genes, including mitochondrial superoxide dismutase. By connecting free radical defense and mitochondrial uncoupling to Akt/FOXO signaling, these results have implications in obesity and type 2 diabetes development and the potential for therapeutic intervention.
Figures




References
-
- Amat R, Solanes G, Giralt M, Villarroya F. SIRT1 is involved in glucocorticoid-mediated control of uncoupling protein-3 gene transcription. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:34066–34076. - PubMed
-
- Barthel A, Schmoll D, Unterman TG. FoxO proteins in insulin action and metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2005;16:183–189. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

