Enhancement of the rate of pyrophosphate hydrolysis by nonenzymatic catalysts and by inorganic pyrophosphatase
- PMID: 21460215
- PMCID: PMC3099670
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.214510
Enhancement of the rate of pyrophosphate hydrolysis by nonenzymatic catalysts and by inorganic pyrophosphatase
Abstract
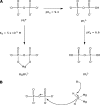
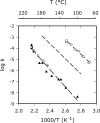
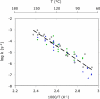
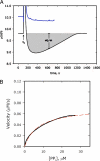
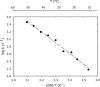
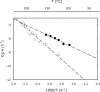
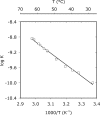
To estimate the proficiency of inorganic pyrophosphatase as a catalyst, (31)P NMR was used to determine rate constants and thermodynamics of activation for the spontaneous hydrolysis of inorganic pyrophosphate (PP(i)) in the presence and absence of Mg(2+) at elevated temperatures. These values were compared with rate constants and activation parameters determined for the reaction catalyzed by Escherichia coli inorganic pyrophosphatase using isothermal titration calorimetry. At 25 °C and pH 8.5, the hydrolysis of MgPP(i)(2-) proceeds with a rate constant of 2.8 × 10(-10) s(-1), whereas E. coli pyrophosphatase was found to have a turnover number of 570 s(-1) under the same conditions. The resulting rate enhancement (2 × 10(12)-fold) is achieved entirely by reducing the enthalpy of activation (ΔΔH(‡) = -16.6 kcal/mol). The presence of Mg(2+) ions or the transfer of the substrate from bulk water to dimethyl sulfoxide was found to increase the rate of pyrophosphate hydrolysis by as much as ∼ 10(6)-fold. Transfer to dimethyl sulfoxide accelerated PP(i) hydrolysis by reducing the enthalpy of activation. Mg(2+) increased the rate of PP(i) hydrolysis by both increasing the entropy of activation and reducing the enthalpy of activation.
Figures

References
-
- Baltscheffsky H., Lundin M., Luxemburg C., Nyren P., Baltscheffsky M. (1986) Chem. Scr. 26B, 259–262
-
- Hedlund J., Cantoni R., Baltscheffsky M., Baltscheffsky H., Persson B. (2006) FEBS J. 273, 5183–5193 - PubMed
-
- Malinen A. M., Belogurov G. A., Baykov A. A., Lahti R. (2007) Biochemistry 46, 8872–8878 - PubMed
-
- Ronimus R. S., Morgan H. W. (2001) Extremophiles 5, 357–373 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

