Distributed structure determination at the JCSG
- PMID: 21460455
- PMCID: PMC3069752
- DOI: 10.1107/S0907444910039934
Distributed structure determination at the JCSG
Abstract
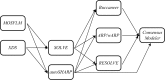
The Joint Center for Structural Genomics (JCSG), one of four large-scale structure-determination centers funded by the US Protein Structure Initiative (PSI) through the National Institute for General Medical Sciences, has been operating an automated distributed structure-solution pipeline, Xsolve, for well over half a decade. During PSI-2, Xsolve solved, traced and partially refined 90% of the JCSG's nearly 770 MAD/SAD structures at an average resolution of about 2 Å without human intervention. Xsolve executes many well established publicly available crystallography software programs in parallel on a commodity Linux cluster, resulting in multiple traces for any given target. Additional software programs have been developed and integrated into Xsolve to further minimize human effort in structure refinement. Consensus-Modeler exploits complementarities in traces from Xsolve to compute a single optimal model for manual refinement. Xpleo is a powerful robotics-inspired algorithm to build missing fragments and qFit automatically identifies and fits alternate conformations.
Figures


References
-
- Adams, P. D. et al. (2010). Acta Cryst. D66, 213–221. - PubMed
-
- Bedem, H. van den, Lotan, I., Latombe, J.-C. & Deacon, A. M. (2005). Acta Cryst. D61, 2–13. - PubMed
-
- Berman, H. M., Henrick, K. & Nakamura, H. (2003). Nature Struct. Biol. 10, 980. - PubMed
-
- Brown, E. N. & Ramaswamy, S. (2007). Acta Cryst. D63, 941–950. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

