Increasing adult hippocampal neurogenesis is sufficient to improve pattern separation
- PMID: 21460835
- PMCID: PMC3084370
- DOI: 10.1038/nature09817
Increasing adult hippocampal neurogenesis is sufficient to improve pattern separation
Abstract
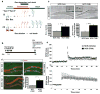
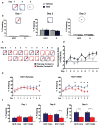
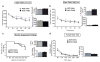
Adult hippocampal neurogenesis is a unique form of neural circuit plasticity that results in the generation of new neurons in the dentate gyrus throughout life. Neurons that arise in adults (adult-born neurons) show heightened synaptic plasticity during their maturation and can account for up to ten per cent of the entire granule cell population. Moreover, levels of adult hippocampal neurogenesis are increased by interventions that are associated with beneficial effects on cognition and mood, such as learning, environmental enrichment, exercise and chronic treatment with antidepressants. Together, these properties of adult neurogenesis indicate that this process could be harnessed to improve hippocampal functions. However, despite a substantial number of studies demonstrating that adult-born neurons are necessary for mediating specific cognitive functions, as well as some of the behavioural effects of antidepressants, it is unknown whether an increase in adult hippocampal neurogenesis is sufficient to improve cognition and mood. Here we show that inducible genetic expansion of the population of adult-born neurons through enhancing their survival improves performance in a specific cognitive task in which two similar contexts need to be distinguished. Mice with increased adult hippocampal neurogenesis show normal object recognition, spatial learning, contextual fear conditioning and extinction learning but are more efficient in differentiating between overlapping contextual representations, which is indicative of enhanced pattern separation. Furthermore, stimulation of adult hippocampal neurogenesis, when combined with an intervention such as voluntary exercise, produces a robust increase in exploratory behaviour. However, increasing adult hippocampal neurogenesis alone does not produce a behavioural response like that induced by anxiolytic agents or antidepressants. Together, our findings suggest that strategies that are designed to increase adult hippocampal neurogenesis specifically, by targeting the cell death of adult-born neurons or by other mechanisms, may have therapeutic potential for reversing impairments in pattern separation and dentate gyrus dysfunction such as those seen during normal ageing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare competing financial interests. R.H is a consultant to Brain Cells Inc. and Astra Zeneca.
Figures

References
-
- Altman J, Das GD. Autoradiographic and histological evidence of postnatal hippocampal neurogenesis in rats. J Comp Neurol. 1965;124:319–335. - PubMed
-
- Eriksson PS, et al. Neurogenesis in the adult human hippocampus. Nat Med. 1998;4:1313–1317. - PubMed
-
- Imayoshi I, et al. Roles of continuous neurogenesis in the structural and functional integrity of the adult forebrain. Nat Neurosci. 2008;11:1153–1161. - PubMed
-
- Gould E, Beylin A, Tanapat P, Reeves A, Shors TJ. Learning enhances adult neurogenesis in the hippocampal formation. Nat Neurosci. 1999;2:260–265. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

