Common variants at ABCA7, MS4A6A/MS4A4E, EPHA1, CD33 and CD2AP are associated with Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 21460840
- PMCID: PMC3084173
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.803
Common variants at ABCA7, MS4A6A/MS4A4E, EPHA1, CD33 and CD2AP are associated with Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
We sought to identify new susceptibility loci for Alzheimer's disease through a staged association study (GERAD+) and by testing suggestive loci reported by the Alzheimer's Disease Genetic Consortium (ADGC) in a companion paper. We undertook a combined analysis of four genome-wide association datasets (stage 1) and identified ten newly associated variants with P ≤ 1 × 10(-5). We tested these variants for association in an independent sample (stage 2). Three SNPs at two loci replicated and showed evidence for association in a further sample (stage 3). Meta-analyses of all data provided compelling evidence that ABCA7 (rs3764650, meta P = 4.5 × 10(-17); including ADGC data, meta P = 5.0 × 10(-21)) and the MS4A gene cluster (rs610932, meta P = 1.8 × 10(-14); including ADGC data, meta P = 1.2 × 10(-16)) are new Alzheimer's disease susceptibility loci. We also found independent evidence for association for three loci reported by the ADGC, which, when combined, showed genome-wide significance: CD2AP (GERAD+, P = 8.0 × 10(-4); including ADGC data, meta P = 8.6 × 10(-9)), CD33 (GERAD+, P = 2.2 × 10(-4); including ADGC data, meta P = 1.6 × 10(-9)) and EPHA1 (GERAD+, P = 3.4 × 10(-4); including ADGC data, meta P = 6.0 × 10(-10)).
Figures
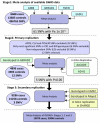


References
-
- Gatz M, et al. Role of genes and environments for explaining Alzheimer disease. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006;63:168–74. - PubMed
-
- Saunders AM, et al. Association of apolipoprotein E allele epsilon 4 with late-onset familial and sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology. 1993;43:1467–72. - PubMed
-
- Lambert JC, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies variants at CLU and CR1 associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Genet. 2009;41:1094–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- G0801306/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U24 AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- G0701075/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U19 AG010483/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- G0902227/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0900688/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0601846/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G9810900/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_G1000734/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0802189/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U123160651/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0300429/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 082604/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

