Phosphorylation of histone H3 serine 28 modulates RNA polymerase III-dependent transcription
- PMID: 21460852
- PMCID: PMC3134635
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2011.105
Phosphorylation of histone H3 serine 28 modulates RNA polymerase III-dependent transcription
Abstract
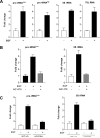
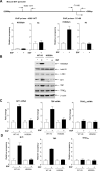
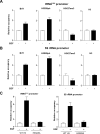
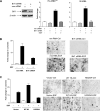
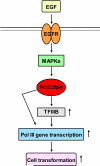
Deregulation of RNA polymerase III (Pol III) transcription enhances cellular tRNAs and 5S rRNA production, leading to an increase in translational capacity to promote cell proliferation, transformation and tumor formation. Phosphorylation of histone H3 (H3ph) is induced by tumor promoters (EGF, UV and TPA) and immediate early genes, such as c-myc, c-jun and c-fos. However, it remains to be determined whether H3ph is involved in RNA Pol III transcription. Here, we report that EGF strongly induced H3ph at serine 28 (H3S28ph). EGF significantly increased transcription of RNA Pol III-dependent genes (Pol III genes), tRNA(Leu), tRNA(Tyr), 5S rRNA and 7SL RNA. Inhibition of EGFR, but not PI3K, reduced both H3S28ph and tRNA(Leu) and 5S rRNA transcription. EGF enhanced occupancy of H3S28ph in the promoters of tRNA(Leu) and 5S rRNA. Further analysis indicates that EGF augmented cellular levels of protein and mRNA of TFIIIB subunits, Brf1 and TATA box-binding protein (TBP). Brf1 is a specific transcription factor for RNA Pol III genes. EGF enhanced occupancy of H3S28ph in the Brf1 and TBP promoters. Inhibition of H3S28ph by mutant H3S28A repressed Brf1, TBP and tRNA(Leu) and 5S rRNA expression and decreased occupancy of H3S28ph in their promoters. Reduction of Brf1 significantly decreased tRNA(Leu) and 5S rRNA transcription and repressed EGF-induced anchorage-independent growth. Blocking H3S28ph signaling by using mutant H3S28A reduced EGF-induced cell transformation. Together, these results indicate that EGF activates EGFR signaling to induce H3S28ph, which, in turn, upregulates tRNA(Leu) and 5S rRNA transcription through Brf1 and TBP and promotes cell transformation. The studies demonstrate that epigenetic modification of H3S28ph has a critical role in the activity of Pol III genes.
Figures

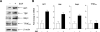
Similar articles
-
Role of phosphorylated histone H3 serine 10 in DEN-induced deregulation of Pol III genes and cell proliferation and transformation.Carcinogenesis. 2013 Nov;34(11):2460-9. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgt219. Epub 2013 Jun 17. Carcinogenesis. 2013. PMID: 23774401 Free PMC article.
-
p53 represses RNA polymerase III transcription by targeting TBP and inhibiting promoter occupancy by TFIIIB.EMBO J. 2003 Jun 2;22(11):2810-20. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg265. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 12773395 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol induces RNA polymerase III-dependent transcription through c-Jun by co-regulating TATA-binding protein (TBP) and Brf1 expression.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jan 28;286(4):2393-401. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.192955. Epub 2010 Nov 24. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21106530 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the RNA polymerase III transcription machinery in Schizosaccharomyces pombe, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and human.Nucleic Acids Res. 2001 Jul 1;29(13):2675-90. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.13.2675. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001. PMID: 11433012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ROS Signaling-Mediated Novel Biological Targets: Brf1 and RNA Pol III Genes.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Oct 4;2021:5888432. doi: 10.1155/2021/5888432. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. Retraction in: Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2024 Jan 9;2024:9890237. doi: 10.1155/2024/9890237. PMID: 34646425 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
Cited by
-
Tamoxifen represses alcohol-induced transcription of RNA polymerase III-dependent genes in breast cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2014 Dec 15;5(23):12410-7. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2678. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 25400119 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring a common mechanism of alcohol-induced deregulation of RNA Pol III genes in liver and breast cells.Gene. 2017 Aug 30;626:309-318. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.05.048. Epub 2017 May 25. Gene. 2017. PMID: 28552569 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol-associated cancer and deregulation of Pol III genes.Gene. 2017 May 15;612:25-28. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2016.09.046. Epub 2016 Sep 30. Gene. 2017. PMID: 27697617 Free PMC article.
-
Fluctuations of Histone Chemical Modifications in Breast, Prostate, and Colorectal Cancer: An Implication of Phytochemicals as Defenders of Chromatin Equilibrium.Biomolecules. 2019 Dec 5;9(12):829. doi: 10.3390/biom9120829. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31817446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of betaine in inhibiting the induction of RNA Pol III gene transcription and cell growth caused by alcohol.Chem Biol Interact. 2020 Jul 1;325:109129. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2020.109129. Epub 2020 May 11. Chem Biol Interact. 2020. PMID: 32418914 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen N, Ma WY, She QB, Wu E, Liu G, Bode AM, Dong Z. Transactivation of the epidermal growth factor receptor is involved in 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:46722–28. - PubMed
-
- Cheung P, Tanner KG, Cheung WL, Sassone-Corsi P, Denu JM, Allis CD. Synergistic coupling of histone H3 phosphorylation and acetylation in response to epidermal growth factor stimulation. Mol Cell. 2000;5:905–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

