N-acetylcysteine and N-nitroarginine methyl ester attenuate Carboplatin-induced ototoxicity in dissociated spiral ganglion neuron cultures
- PMID: 21461057
- PMCID: PMC3062221
- DOI: 10.3342/ceo.2011.4.1.11
N-acetylcysteine and N-nitroarginine methyl ester attenuate Carboplatin-induced ototoxicity in dissociated spiral ganglion neuron cultures
Abstract
Objectives: Carboplatin, a platinum-containing anti-cancer drug used to treat a variety of cancers, induces ototoxicity. Since, reactive oxygen species (ROS) and nitric oxide (NO) seem to be responsible for this toxicity, the antioxidant, N-acetyl-L-cysteine (L-NAC), and NO synthetase inhibitor, N-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) were predicted to have protective effects against carboplatin ototoxicity. The aim of this study was to test for the protective effects of L-NAC and L-NAME on cochlear hair cells and spiral ganglion neurons (SGNs).
Methods: Cochlear organotypic cultures and dissociated spiral ganglion neuron cultures, from mice postnatal day 5 cultures were used in this study. The cultures were treated with carboplatin alone or in combination with L-NAC or L-NAME, and carboplatin-induced damage was monitored.
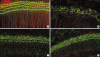
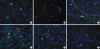
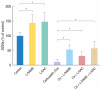
Results: Treatment with carboplatin induced a significant loss of outer hair cells, while inner hair cells were preserved in the cochlear organotypic cultures. Addition of L-NAC or L-NAME reduced the amount of carboplatin-induced hair cell damage; the differences did not reach statistical significance. However, carboplatin significantly decreased the number of surviving SGNs in dissociated cultures. The toxic effects were significantly reduced by addition of L-NAC or L-NAME. In addition, carboplatin induced the loss of neurites from the SGN somata, and this was not blocked with L-NAC or L-NAME.
Conclusion: The results of this study suggest that ROS and NO are involved in carboplatin-induced damage to hair cells and SGNs, and administration of L-NAC/L-NAME can be used to attenuate the toxicity.
Keywords: Carboplatin; Inner hair cell; Mouse; Nitric oxide; Ototoxicity; Outer hair cell; Spiral ganglion neuron.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
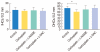
Similar articles
-
OTOTOXIC EFFECTS OF CARBOPLATIN IN ORGANOTYPIC CULTURES IN CHINCHILLAS AND RATS.J Otol. 2012 Dec;7(2):92-101. doi: 10.1016/S1672-2930(12)50023-1. J Otol. 2012. PMID: 25593588 Free PMC article.
-
PRDX1 activates autophagy via the PTEN-AKT signaling pathway to protect against cisplatin-induced spiral ganglion neuron damage.Autophagy. 2021 Dec;17(12):4159-4181. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2021.1905466. Epub 2021 Apr 12. Autophagy. 2021. PMID: 33749526 Free PMC article.
-
L-n-acetyl-cysteine protection against cisplatin-induced auditory neuronal and hair cell toxicity.Laryngoscope. 2001 Jul;111(7):1147-55. doi: 10.1097/00005537-200107000-00005. Laryngoscope. 2001. PMID: 11568534
-
Selective loss of inner hair cells and type-I ganglion neurons in carboplatin-treated chinchillas. Mechanisms of damage and protection.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999 Nov 28;884:152-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1999.tb08640.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999. PMID: 10842592 Review.
-
Neurochemistry of the peripheral and central auditory system after ototoxic drug exposure: implications for tinnitus.Int Tinnitus J. 2005;11(1):23-30. Int Tinnitus J. 2005. PMID: 16419684 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeted Delivery of Doxorubicin via CD147-Mediated ROS/pH Dual-Sensitive Nanomicelles for the Efficient Therapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.AAPS J. 2018 Feb 23;20(2):34. doi: 10.1208/s12248-018-0195-8. AAPS J. 2018. PMID: 29476273
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress is involved in the response of human laryngeal carcinoma cells to Carboplatin but is absent in Carboplatin-resistant cells.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 23;8(9):e76397. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076397. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24086737 Free PMC article.
-
Methylseleninic acid sensitizes Notch3-activated OVCA429 ovarian cancer cells to carboplatin.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 10;9(7):e101664. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101664. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25010594 Free PMC article.
-
Ameliorative Effect of Coenzyme Q10 and/or Candesartan on Carboplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity: Roles of Apoptosis, Transforming Growth Factor-Β1, Nuclear Factor Kappa-B And The Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2017 Jun 25;18(6):1629-1636. doi: 10.22034/APJCP.2017.18.6.1629. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2017. PMID: 28670881 Free PMC article.
-
Cisplatin-Induced Hearing Loss, Oxidative Stress, and Antioxidants as a Therapeutic Strategy-A State-of-the-Art Review.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Dec 21;13(12):1578. doi: 10.3390/antiox13121578. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39765905 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahmed SM, Cohen EE. Treatment of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck in the metastatic and refractory settings: advances in chemotherapy and the emergence of small molecule epidermal growth factor receptor kinase inhibitors. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2007 Nov;7(7):666–673. - PubMed
-
- Goffin J, Lacchetti C, Ellis PM, Ung YC, Evans WK Lung Cancer Disease Site Group of Cancer Care Ontarios Program in Evidence-Based Care. First-line systemic chemotherapy in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review. J Thorac Oncol. 2010 Feb;5(2):260–274. - PubMed
-
- Marchetti C, Pisano C, Facchini G, Bruni GS, Magazzino FP, Losito S, et al. First-line treatment of advanced ovarian cancer: current research and perspectives. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2010 Jan;10(1):47–60. - PubMed
-
- Esteban-Fernandez D, Verdaguer JM, Ramirez-Camacho R, Palacios MA, Gomez-Gomez MM. Accumulation, fractionation, and analysis of platinum in toxicologically affected tissues after cisplatin, oxaliplatin, and carboplatin administration. J Anal Toxicol. 2008 Mar;32(2):140–146. - PubMed

