Temozolomide modifies caveolin-1 expression in experimental malignant gliomas in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 21461172
- PMCID: PMC3069652
- DOI: 10.1593/tlo.10205
Temozolomide modifies caveolin-1 expression in experimental malignant gliomas in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
Background: Caveolin-1 is a protein that displays promotive versus preventive roles in cancer progression according to circumstances. Temozolomide (TMZ) is the standard chemotherapeutic to treat glioma patients. The present work aims to characterizeTMZ-induced effects on caveolin-1 expression in glioma cells.
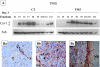
Methods: Human astroglioma (U373 and T98G) and oligodendroglioma (Hs683) cell lines were used in vitro as well as in vivo orthotopic xenografts (Hs683 and U373) into the brains of immunocompromisedmice. In vitro TMZ-induced effects on protein expression and cellular localization were determined by Western blot analysis and on the actin cytoskeleton organization by means of immunofluorescence approaches. In vivo TMZ-induced effects in caveolin-1 expression in human glioma xenografts were monitored by means of immunohistochemistry.
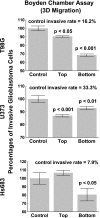
Results: TMZ modified caveolin-1 expression and localization in vitro and in vivo after an administration schedule that slightly, if at all, impaired cell growth characteristics in vitro. Caveolin-1 by itself (at a 100-ng/ml concentration) was able to significantly reduce invasiveness (Boyden chambers) of the three human glioma cell lines. The TMZ-inducedmodification in caveolin-1 expression in flotation/raft compartments was paralleled by altered Cyr61 and β(1) integrin expression, two elements that have already been reported to collaborate with caveolin-1 in regulating glioma cell biology, and all these features led to profound reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton. An experimental Src kinase inhibitor, AZD0530, almost completely antagonized the TMZ-induced modulation in caveolin-1 expression.
Conclusion: TMZ modifies caveolin-1 expression in vitro and in vivo in glioma cells, a feature that directly affects glioma cell migration properties.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Temozolomide-induced modification of the CXC chemokine network in experimental gliomas.Int J Oncol. 2011 May;38(5):1453-64. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2011.964. Epub 2011 Mar 8. Int J Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21399866
-
Evaluation of the efficiency of chemotherapy in in vivo orthotopic models of human glioma cells with and without 1p19q deletions and in C6 rat orthotopic allografts serving for the evaluation of surgery combined with chemotherapy.Cancer. 2002 Aug 1;95(3):641-55. doi: 10.1002/cncr.10710. Cancer. 2002. PMID: 12209758
-
Long-term in vitro treatment of human glioblastoma cells with temozolomide increases resistance in vivo through up-regulation of GLUT transporter and aldo-keto reductase enzyme AKR1C expression.Neoplasia. 2010 Sep;12(9):727-39. doi: 10.1593/neo.10526. Neoplasia. 2010. PMID: 20824049 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term temozolomide treatment induces marked amino metabolism modifications and an increase in TMZ sensitivity in Hs683 oligodendroglioma cells.Neoplasia. 2010 Jan;12(1):69-79. doi: 10.1593/neo.91360. Neoplasia. 2010. PMID: 20072655 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of levetiracetam and IFN-α increased temozolomide efficacy in MGMT-positive glioma.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2020 Dec;86(6):773-782. doi: 10.1007/s00280-020-04169-y. Epub 2020 Oct 19. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33074386
Cited by
-
Valproic acid downregulates the expression of MGMT and sensitizes temozolomide-resistant glioma cells.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012:987495. doi: 10.1155/2012/987495. Epub 2012 Jun 4. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22701311 Free PMC article.
-
Polymerase I and transcript release factor acts as an essential modulator of glioblastoma chemoresistance.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 18;9(4):e93439. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0093439. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24747515 Free PMC article.
-
Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Prevent Therapeutic Escape in Breast Cancer Cells.Mol Cancer Ther. 2016 Sep;15(9):2198-208. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0813. Epub 2016 Jun 2. Mol Cancer Ther. 2016. PMID: 27256378 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal transfer of miR-1238 contributes to temozolomide-resistance in glioblastoma.EBioMedicine. 2019 Apr;42:238-251. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.03.016. Epub 2019 Mar 24. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 30917935 Free PMC article.
-
Caveolin-1 is a negative regulator of tumor growth in glioblastoma and modulates chemosensitivity to temozolomide.Cell Cycle. 2013 May 15;12(10):1510-20. doi: 10.4161/cc.24497. Epub 2013 Apr 17. Cell Cycle. 2013. PMID: 23598719 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lefranc F, Sadeghi N, Camby I, Metens T, Dewitte O, Kiss R. Present and potential future issues in glioblastoma treatment. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2006;6:719–732. - PubMed
-
- Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Taphoorn MJ, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Allgeier A, Fisher B, Belanger K, et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:459–466. - PubMed
-
- Lefranc F, Brotchi J, Kiss R. Possible future issues in the treatment of glioblastomas: special emphasis on cell migration and the resistance of migrating glioblastoma cells to apoptosis. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:2411–2422. - PubMed
-
- Le Calvé B, Rynkowski M, Le Mercier M, Bruyère C, Lonez C, Gras T, Haibe-Kains B, Bontempi G, Decaestecker C, Ruysschaert JM, et al. Long term in vitro treatment of human glioblastoma cells with temozolomide confers resistance in vivo through up-regulation of GLUT transporter and aldo-keto reductase enzyme AKR1C expression. Neoplasia. 2010;12:727–739. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hegi ME, Liu L, Herman JG, Stupp R, Wick W, Weller M, Mehta MP, Gilbert MR. Correlation of O6-methylguanine methyltransferase (MGMT) promoter methylation with clinical outcomes in glioblastoma and clinical strategies to modulate MGMTactivity. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:4189–4199. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
