Sleep disordered breathing with excessive daytime sleepiness is a risk factor for mortality in older adults
- PMID: 21461321
- PMCID: PMC3065253
- DOI: 10.1093/sleep/34.4.435
Sleep disordered breathing with excessive daytime sleepiness is a risk factor for mortality in older adults
Abstract
Study objectives: Excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS) is associated with increased mortality in older adults, yet sleep disordered breathing (SDB), a common cause of sleepiness, has not been shown to increase mortality in older adults. This study examined the relationship between daytime sleepiness, SDB, self-report sleep parameters, and mortality in older adults.
Design: Longitudinal cohort study.
Setting: Clinical and Translational Research Center, at-home testing.
Participants: 289 study participants (age >65, no dementia or depression at the time of enrollment) classified as having EDS (n=146) or not (n=143).
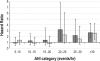
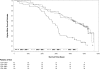
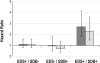
Measurements and results: Study participants underwent in-lab polysomnography and multiple sleep latency testing at cohort inception. Survival analysis was conducted, with an average follow-up of 13.8 years. Excessive daytime sleepiness was associated with an unadjusted mortality hazard ratio of 1.5 (95% CI 1.1-2.0). The unadjusted mortality hazard ratio for study participants with both EDS and SDB (apnea-hypopnea index ≥20 events/h) was 2.7, 95% CI: 1.8-4.2. These findings persisted with an adjusted mortality hazard ratio of 2.3, 95% CI: 1.5-3.6 in the final model that included other covariates associated with increased mortality (sleep duration >8.5 h, self-reported angina, male gender, African American race, and age).
Conclusion: The presence of SDB is an important risk factor for mortality from excessive daytime sleepiness in older adults. In the presence of SDB at an AHI ≥20 events/h, EDS was associated with an increased all-cause mortality risk in older adults, even when adjusting for other significant risk factors, such as prolonged sleep duration. In older patients who had SDB without EDS, or EDS without SDB, there was no increased all-cause mortality rate.
Keywords: Sleep disordered breathing; aged; daytime sleepiness; longitudinal; mortality.
Figures
Comment in
-
Sleep disordered breathing and subjective sleepiness in the elderly: a deadly combination?Sleep. 2011 Apr 1;34(4):413-5. doi: 10.1093/sleep/34.4.413. Sleep. 2011. PMID: 21461318 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Foley DJ, Vitiello MV, Bliwise DL, Ancoli-Israel S, Monjan AA, Walsh JK. Frequent napping is associated with excessive daytime sleepiness, depression, pain, and nocturia in older adults: findings from the National Sleep Foundation “2003 Sleep in America” Poll. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2007;15:344–50. - PubMed
-
- Hays JC, Blazer DG, Foley DJ. Risk of napping: excessive daytime sleepiness and mortality in an older community population. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1996;44:693–8. - PubMed
-
- Gooneratne NS, Weaver TE, Cater JR, et al. Functional outcomes of excessive daytime sleepiness in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2003;51:642–9. - PubMed
-
- Lee JH, Bliwise DL, Ansari FP, et al. Daytime sleepiness and functional impairment in Alzheimer disease. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2007;15:620–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

