Statins: cardiovascular risk reduction in percutaneous coronary intervention-basic and clinical evidence of hyperacute use of statins
- PMID: 21461336
- PMCID: PMC3065660
- DOI: 10.4061/2011/904742
Statins: cardiovascular risk reduction in percutaneous coronary intervention-basic and clinical evidence of hyperacute use of statins
Abstract
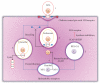
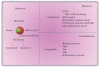
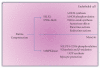
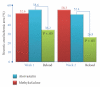
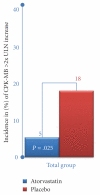
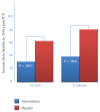
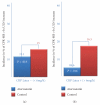
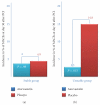
Reduction of LDL-cholesterol concentration in serum, blocking the isoprenylation of GTPases and the activation of myocyte-protective enzyme systems are three mechanisms that currently explain the lipid and non-lipid effects of statins. However, the decrease of LDL-cholesterol, the reduction of inflammation biomarkers and even the atheroregresion, as surrogate effects to the mechanisms of action of statins would be irrelevant if not accompanied by a significant decrease in the incidence of cardiovascular events. Statins like no other pharmacological group have proven to reduce the incidence of cardiovascular events and prolong life in any clinical scenario. This article review the basic and clinical evidence that support a new indication for HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors "pharmacological myocardial preconditioning before anticipated ischemia" or hyperacute use of statins in subjects with any coronary syndrome eligible for elective, semi-urgent or primary percutaneous coronary intervention: ARMYDA-Original, NAPLES I-II, ARMYDA-ACS, ARMYDA-RECAPTURE, Non-STEMI-Korean, Korean-STEMI trials.
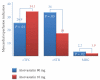
Figures
Similar articles
-
Atorvastatin efficacy in the primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular events.Drugs. 2007;67 Suppl 1:29-42. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200767001-00004. Drugs. 2007. PMID: 17910519 Review.
-
Pleiotropic effects of statins: evidence against benefits beyond LDL-cholesterol lowering.Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2010;10 Suppl 1:10-7. doi: 10.2165/1158822-S0-000000000-00000. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2010. PMID: 21391729 Review.
-
Policosanol safely down-regulates HMG-CoA reductase - potential as a component of the Esselstyn regimen.Med Hypotheses. 2002 Sep;59(3):268-79. doi: 10.1016/s0306-9877(02)00226-8. Med Hypotheses. 2002. PMID: 12208152
-
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Similarities and differences.Clin Pharmacokinet. 1997 May;32(5):403-25. doi: 10.2165/00003088-199732050-00005. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1997. PMID: 9160173 Review.
-
Percutaneous coronary interventions and statins therapy.Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2008 Apr;2(2):101-7. doi: 10.1177/1753944708089983. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2008. PMID: 19124413 Review.
Cited by
-
Differences in statin usage and target-goal achievement between departments at the same hospital.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e50466. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050466. Epub 2012 Dec 10. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23251371 Free PMC article.
-
Poor maternal nutrition programmes a pro-atherosclerotic phenotype in ApoE-/- mice.Clin Sci (Lond). 2012 Aug 1;123(4):251-7. doi: 10.1042/CS20110487. Clin Sci (Lond). 2012. PMID: 22375564 Free PMC article.
-
Statins for COPD: a challenge to conventional beliefs?Prim Care Respir J. 2012 Mar;21(1):5-7. doi: 10.4104/pcrj.2012.00020. Prim Care Respir J. 2012. PMID: 22349920 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The challenge of translating ischemic conditioning from animal models to humans: the role of comorbidities.Dis Model Mech. 2014 Dec;7(12):1321-33. doi: 10.1242/dmm.016741. Dis Model Mech. 2014. PMID: 25481012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An overview of protective strategies against ischemia/reperfusion injury: The role of hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning.Brain Behav. 2018 Mar 30;8(5):e00959. doi: 10.1002/brb3.959. eCollection 2018 May. Brain Behav. 2018. PMID: 29761012 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Endo A. The discovery and development of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Journal of Lipid Research. 1992;33(11):1569–1582. - PubMed
-
- Brown MS, Goldstein JL. A tribute to Akira Endo, discoverer of a “Penicillin” for the cholesterol. Atherosclerosis Supplements. 2004;(5):13–16. - PubMed
-
- Brown MS, Goldstein JL. A receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science. 1986;232(4746):34–47. - PubMed
-
- Goldstein JL, Brown MS. Regulation of the mevalonate pathway. Nature. 1990;343(6257):425–430. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

