Clinical utility of serum interleukin-8 and interferon-alpha in thyroid diseases
- PMID: 21461397
- PMCID: PMC3065012
- DOI: 10.4061/2011/270149
Clinical utility of serum interleukin-8 and interferon-alpha in thyroid diseases
Abstract
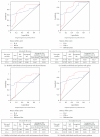
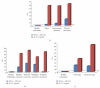
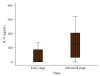
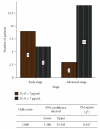
Serum interleukin-8 (IL-8) and interferon-alpha (IFN-α) levels have been estimated from a total of 88 individuals of which 19 were disease-free healthy individuals, and 69 were patients with thyroid diseases: goitre (N = 21), autoimmune diseases (N = 16), and carcinomas (N = 32). Both IL-8 and IFN-α were significantly higher in all the patients as compared to healthy individuals. Serum IL-8 levels showed significant positive correlation with disease stage in thyroid cancer patients. Higher serum IL-8 levels were associated with advanced disease stage while no significant correlation was observed between serum IFN-α levels and any of the clinicopathological parameters. IL-8 and IFN-α significantly correlated with each other in anaplastic carcinoma patients. Finally concluding, monitoring the serum IL-8 and IFN-α levels can help differentiate patients with thyroid diseases from healthy individuals, and IL-8 seems to have a role in the pathogenesis of thyroid diseases and may represent a target for innovative diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.
Figures

References
-
- Venkatesh YS, Ordonez NG, Schultz PN, Hickey RC, Goepfert H, Samaan NA. Anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid. A clinicopathologic study of 121 cases. Cancer. 1990;66(2):321–330. - PubMed
-
- Carcangiu ML, Steeper T, Zampi G, Rosai J. Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma: a study of 70 cases. American Journal of Clinical Pathology. 1985;83(2):135–158. - PubMed
-
- Ron E. Epidemiology of thyroid cancer. In: Schottenfeld D, Fraumeni JR Jr., editors. Cancer Epidemiology and Prevention. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press; 1996. pp. 1000–1021.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

