Capillary isoelectric focusing with pH 9.7 cathode for the analysis of gastric biopsies
- PMID: 21461616
- PMCID: PMC4429874
- DOI: 10.1007/s00216-011-4926-2
Capillary isoelectric focusing with pH 9.7 cathode for the analysis of gastric biopsies
Abstract
Capillary isoelectric focusing tends to suffer from poor reproducibility, particularly for the analysis of complex protein samples from cellular or tissue homogenates. This poor reproducibility appears to be associated with erratic variations in electroosmotic flow. One cause of electroosmotic flow variation is degradation of the capillary coating caused by the extremely basic solution commonly used during mobilization and focusing; this degradation of the capillary coating can be reduced by employing a CAPS mobilization buffer at pH 9. Another cause of variation is protein adsorption to the capillary wall, which causes an increase in electroosmotic flow. The effects of protein adsorption can be reduced by use of surfactants in the buffer and by employing an extremely low sample loading. We report the use of CAPS mobilization buffer in combination with an ultrasensitive laser-induced fluorescence detector for the reproducible analysis of ∼2 ng of protein from a Barrett's esophagus biopsy.
Figures
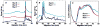
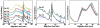
Similar articles
-
Capillary isoelectric focusing method development and validation for investigation of recombinant therapeutic monoclonal antibody.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2015 Oct 10;114:53-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2015.04.037. Epub 2015 May 6. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2015. PMID: 26025812
-
Capillary array isoelectric focusing with laser-induced fluorescence detection: milli-pH unit resolution and yoctomole mass detection limits in a 32-channel system.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010 Aug;397(8):3305-10. doi: 10.1007/s00216-010-3595-x. Epub 2010 Mar 25. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010. PMID: 20336452 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of catholytes on the mobilization of proteins after capillary isoelectric focusing.Electrophoresis. 1997 Jan;18(1):92-7. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150180118. Electrophoresis. 1997. PMID: 9059828
-
The biopsy diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease, "carditis," and Barrett's esophagus, and sequelae of therapy.Am J Surg Pathol. 1996;20 Suppl 1:S31-50. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199600001-00005. Am J Surg Pathol. 1996. PMID: 8694147 Review.
-
Recent developments in capillary isoelectric focusing with whole-column imaging detection.Electrophoresis. 1998 Oct;19(13):2290-5. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150191307. Electrophoresis. 1998. PMID: 9788311 Review.
Cited by
-
A Mini Review on Capillary Isoelectric Focusing-Mass Spectrometry for Top-Down Proteomics.Front Chem. 2021 Apr 9;9:651757. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2021.651757. eCollection 2021. Front Chem. 2021. PMID: 33898392 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trajectory of isoelectric focusing from gels to capillaries to immobilized gradients in capillaries.Proteomics. 2012 Oct;12(19-20):2918-26. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201200213. Epub 2012 Sep 24. Proteomics. 2012. PMID: 22930445 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wu J, Pawliszyn J. Fast Analysis of Proteins by Isoelectric-Focusing Performed in Capillary Array Detected with Concentration Gradient Imaging-System. Electrophoresis. 1993;14:469–474. - PubMed
-
- Wu J, Pawliszyn J. Isoelectric-Focusing of Proteins in a Microcapillary with Universal Concentration Gradient Detection. J Microcolumn. 1992 Sep 4;:419–422.
-
- Dou P, Liu Z, He JG, Xu JJ, Chen HY. Rapid and high-resolution glycoform profiling of recombinant human erythropoietin by capillary isoelectric focusing with whole column imaging detection. J Chromatogr A. 2008;1190:372–376. - PubMed
-
- Shen YF, Xiang F, Veenstra TD, Fung EN, Smith RD. High-resolution capillary isoelectric focusing of complex protein mixtures from lysates of microorganisms. Anal Chem. 1999;71:5348–5353. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

