Phylogenetic analysis of protein sequences based on distribution of length about common sub-string
- PMID: 21461804
- PMCID: PMC7088358
- DOI: 10.1007/s10930-011-9318-0
Phylogenetic analysis of protein sequences based on distribution of length about common sub-string
Abstract
Up to now, various approaches for phylogenetic analysis have been developed. Almost all of them put stress on analyzing nucleic acid sequences or protein primary sequences. In this paper, we propose a new sequence distance for efficient reconstruction of phylogenetic trees based on the distribution of length about common sub-sequences between two sequences. We describe some applications of this method, which not only show the validity of the method, but also suggest a number of novel phylogenetic insights.
Figures
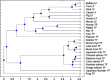
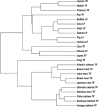

Similar articles
-
2-D graphical representation of protein sequences and its application to coronavirus phylogeny.BMB Rep. 2008 Mar 31;41(3):217-22. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2008.41.3.217. BMB Rep. 2008. PMID: 18377725
-
Nucleotide sequence and expression of the spike (S) gene of canine coronavirus and comparison with the S proteins of feline and porcine coronaviruses.J Gen Virol. 1994 Jul;75 ( Pt 7):1789-94. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-75-7-1789. J Gen Virol. 1994. PMID: 8021609
-
Evidence for a common evolutionary origin of coronavirus spike protein receptor-binding subunits.J Virol. 2012 Mar;86(5):2856-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06882-11. Epub 2011 Dec 28. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22205743 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogenomics and bioinformatics of SARS-CoV.Trends Microbiol. 2004 Mar;12(3):106-11. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2004.01.005. Trends Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15058277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Receptor specificity and receptor-induced conformational changes in mouse hepatitis virus spike glycoprotein.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2001;494:173-81. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-1325-4_29. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2001. PMID: 11774465 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Protein Sequence Comparison Based on Physicochemical Properties and the Position-Feature Energy Matrix.Sci Rep. 2017 Apr 10;7:46237. doi: 10.1038/srep46237. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28393857 Free PMC article.
-
Development of an antimicrobial resistance plasmid transfer gene database for enteric bacteria.Front Bioinform. 2023 Nov 14;3:1279359. doi: 10.3389/fbinf.2023.1279359. eCollection 2023. Front Bioinform. 2023. PMID: 38033626 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying anticancer peptides by using a generalized chaos game representation.J Math Biol. 2019 Jan;78(1-2):441-463. doi: 10.1007/s00285-018-1279-x. Epub 2018 Oct 5. J Math Biol. 2019. PMID: 30291366
-
Information properties of naturally-occurring proteins: Fourier analysis and complexity phase plots.Protein J. 2012 Oct;31(7):550-63. doi: 10.1007/s10930-012-9432-7. Protein J. 2012. PMID: 22814572
-
A new bioinformatics approach to natural protein collections: permutation structure contrasts of viral and cellular systems.Protein J. 2013 Apr;32(4):275-87. doi: 10.1007/s10930-013-9485-2. Protein J. 2013. PMID: 23605224
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

