Chemomechanical coupling and motor cycles of myosin V
- PMID: 21463588
- PMCID: PMC3072604
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2011.02.012
Chemomechanical coupling and motor cycles of myosin V
Abstract
The molecular motor myosin V has been studied extensively both in bulk and single molecule experiments. Based on the chemical states of the motor, we construct a systematic network theory that includes experimental observations about the stepping behavior of myosin V. We utilize constraints arising from nonequilibrium thermodynamics to determine motor parameters and demonstrate that the motor behavior is governed by three chemomechanical motor cycles. The competition between these cycles can be understood via the influence of external load forces onto the chemical transition rates for the binding of adenosine triphosphate and adenosine diphosphate. In addition, we also investigate the functional dependence of the mechanical stepping rates on these forces. For substall forces, the dominant pathway of the motor network is profoundly different from the one for superstall forces, which leads to a stepping behavior that is in agreement with the experimental observations. Our theory provides a unified description of the experimental data as obtained for myosin V in single motor experiments.
Copyright © 2011 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


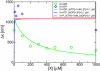
 , and M. The chemomechanical forward cycle F consists of the states 〈1234′〉, which contain both chemical and mechanical transitions, while the dissipative or enzymatic slip cycle
, and M. The chemomechanical forward cycle F consists of the states 〈1234′〉, which contain both chemical and mechanical transitions, while the dissipative or enzymatic slip cycle  with states 〈256〉 is purely chemical. The ratcheting cycle M, on the other hand, consists only of the mechanical stepping transitions |55′〉, |5′5″〉, and so on. Each state is characterized by the chemical composition of the two motor heads, the one on the right-hand side being the leading one. The solid lines (blue) are the chemical transitions for the indicated species X = ATP, ADP, or P, while the broken lines (red) show the stepping transitions. The arrows refer to the direction of forward stepping and ATP hydrolysis, respectively.
with states 〈256〉 is purely chemical. The ratcheting cycle M, on the other hand, consists only of the mechanical stepping transitions |55′〉, |5′5″〉, and so on. Each state is characterized by the chemical composition of the two motor heads, the one on the right-hand side being the leading one. The solid lines (blue) are the chemical transitions for the indicated species X = ATP, ADP, or P, while the broken lines (red) show the stepping transitions. The arrows refer to the direction of forward stepping and ATP hydrolysis, respectively.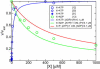


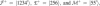

References
-
- Mehta A.D., Rock R.S., Cheney R.E. Myosin-V is a processive actin-based motor. Nature. 1999;400:590–593. - PubMed
-
- Yildiz A., Forkey J.N., Selvin P.R. Myosin V walks hand-over-hand: single fluorophore imaging with 1.5-nm localization. Science. 2003;300:2061–2065. - PubMed
-
- Veigel C., Wang F., Molloy J.E. The gated gait of the processive molecular motor, myosin V. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002;4:59–65. - PubMed
-
- Veigel C., Schmitz S., Sellers J.R. Load-dependent kinetics of myosin-V can explain its high processivity. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005;7:861–869. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

