Memory cells specific for myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG) govern the transfer of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
- PMID: 21463904
- PMCID: PMC3690522
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2011.02.008
Memory cells specific for myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG) govern the transfer of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
Abstract
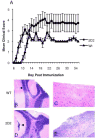
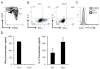
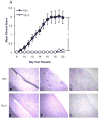
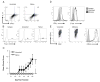
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an inflammatory disease of the CNS mediated by CD4(+) T cells directed against myelin antigens. Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) is induced by immunization with myelin antigens like myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG). We have explored the transfer of EAE using MOG(35-55)-specific TCR transgenic (2D2) T cells. Unsorted 2D2 Th1 cells reliably transferred EAE. Further, we found that CD44(hi)CD62L(lo) effector/memory CD4(+) T cells are likely responsible for the disease transfer due to the up-regulation of CD44. Given the importance of MOG in MS pathogenesis, mechanistic insights into adoptively transferred EAE by MOG-specific Th1 cells could prove valuable in MS research.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
De novo central nervous system processing of myelin antigen is required for the initiation of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.J Immunol. 2002 Apr 15;168(8):4173-83. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.8.4173. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11937578
-
Studies in B7-deficient mice reveal a critical role for B7 costimulation in both induction and effector phases of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.J Exp Med. 1999 Sep 6;190(5):733-40. doi: 10.1084/jem.190.5.733. J Exp Med. 1999. PMID: 10477557 Free PMC article.
-
Lymph node-derived donor encephalitogenic CD4+ T cells in C57BL/6 mice adoptive transfer experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis highly express GM-CSF and T-bet.J Neuroinflammation. 2011 Jun 24;8:73. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-8-73. J Neuroinflammation. 2011. PMID: 21702922 Free PMC article.
-
Control of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by CD4+ suppressor T cells: peripheral versus in situ immunoregulation.J Neuroimmunol. 2007 Nov;191(1-2):61-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2007.09.010. Epub 2007 Sep 27. J Neuroimmunol. 2007. PMID: 17900707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Origins and significance of astrogliosis in the multiple sclerosis model, MOG peptide EAE.J Neurol Sci. 2013 Oct 15;333(1-2):55-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2012.12.014. Epub 2013 Jan 5. J Neurol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23294494 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Trichloroethylene-induced alterations in DNA methylation were enriched in polycomb protein binding sites in effector/memory CD4+ T cells.Environ Epigenet. 2017 Jul;3(3):dvx013. doi: 10.1093/eep/dvx013. Epub 2017 Sep 6. Environ Epigenet. 2017. PMID: 29129997 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo modification of tRNA with an artificial nucleobase leads to full disease remission in an animal model of multiple sclerosis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Feb 28;45(4):2029-2039. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw847. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28204548 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial TWIK-related potassium channel-1 (TREK1) regulates immune-cell trafficking into the CNS.Nat Med. 2013 Sep;19(9):1161-5. doi: 10.1038/nm.3303. Epub 2013 Aug 11. Nat Med. 2013. PMID: 23933981
-
Immunosuppressive potential of human amnion epithelial cells in the treatment of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.J Neuroinflammation. 2015 Jun 3;12:112. doi: 10.1186/s12974-015-0322-8. J Neuroinflammation. 2015. PMID: 26036872 Free PMC article.
-
Th40 cells (CD4+CD40+ Tcells) drive a more severe form of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis than conventional CD4 T cells.PLoS One. 2017 Feb 13;12(2):e0172037. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172037. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28192476 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bebo BF, Jr, Schuster JC, Vandenbark AA, Offner H. Androgens alter the cytokine profile and reduce encephalogenicity of myelin-reactive T cells. J Immunol. 1999;162:35–40. - PubMed
-
- Bettelli E, Carrier Y, Gao W, Korn T, Strom TB, Oukka M, Weiner HL, Kuchroo VK. Reciprocal developmental pathways for the generation of pathogenic effector TH17 and regulatory T cells. Nature. 2006;441:235–238. - PubMed
-
- Bielekova B, Goodwin B, Richert N, Cortese I, Kondo T, Afshar G, Gran B, Eaton J, Antel J, Frank JA, McFarland HF, Martin R. Encephalitogenic potential of the myelin basic protein peptide (amino acids 83-99) in multiple sclerosis: results of a phase II clinical trial with an altered peptide ligand. Nat Med. 2000;6:1167–1175. - PubMed
-
- Brocke S, Piercy C, Steinman L, Weissman IL, Veromaa T. Antibodies to CD44 and integrin α4, but not L-selectin, prevent central nervous system inflammation and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by blocking secondary leukocyte recruitment. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96:6896–6901. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

