Induction of retinoid X receptor activity and consequent upregulation of p21WAF1/CIP1 by indenoisoquinolines in MCF7 cells
- PMID: 21464033
- PMCID: PMC5554444
- DOI: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-10-0004
Induction of retinoid X receptor activity and consequent upregulation of p21WAF1/CIP1 by indenoisoquinolines in MCF7 cells
Abstract
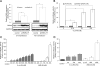
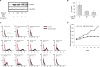
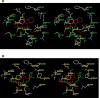
Retinoid X receptor (RXR) has been targeted for the chemoprevention and treatment of cancer. To discover potential agents acting through RXRs, we utilized an RXR response element (RXRE)-luciferase reporter gene assay. Following extensive screening, 3-amino-6-(3-aminopropyl)-5,6-dihydro-5,11-dioxo-11H-indeno[1,2-c]isoquinoline dihydrochloride (AM6-36) was found to induce RXRE-luciferase activities. AM6-36 inhibited COX-2 expression and anchorage-independent growth with 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate-stimulated JB6 Cl41 cells, induced the expression of CD38 in HL-60 cells, and attenuated the growth of N-methyl-N-nitrosourea-induced mammary tumors in rats. Consistent with other reports describing the antiproliferative effects of RXR agonists in breast cancers, AM6-36 showed growth inhibition with cultured MCF7 breast cancer cells, accompanied by G(2)/M-phase arrest at lower concentrations and enhanced S-phase arrest at higher concentrations. On the basis of DNA microarray analysis, AM6-36 upregulated the expression of CDKN1A, a target gene of RXR, by 35-fold. In accord with this response, the expression of the corresponding protein, p21(WAF1/CIP1), was increased in the presence of AM6-36. Induction of p21 by AM6-36 was abrogated following transient knockdown of RXRα, demonstrating that the effect of AM6-36 on the expression of p21 is closely related to modulation of RXRα transcriptional activity. Intestinal permeability was suggested with Caco-2 cells and limited metabolism resulted when AM6-36 was incubated with human liver microsomes. Oral administration with rats resulted in 0.8 μg/mL, 4.3 μg/g, and 0.3 μg/g in serum, liver, and mammary gland, respectively. In sum, these data suggest that AM6-36 is a promising lead for the treatment or prevention of breast cancer and provide a strong rationale for testing in more advanced antitumor systems.
©2011 AACR.
Figures


References
-
- Mangelsdorf DJ, Ong ES, Dyck JA, Evans RM. Nuclear receptor that identifies a novel retinoic acid response pathway. Nature. 1990;345:224–9. - PubMed
-
- Szanto A, Narkar V, Shen Q, Uray IP, Davies PJ, Nagy L. Retinoid X receptors: X-ploring their (patho)physiological functions. Cell Death Differ. 2004;11:S126–43. - PubMed
-
- Mangelsdorf DJ, Evans RM. The RXR heterodimers and orphan receptors. Cell. 1995;83:841–50. - PubMed
-
- Wolf G. Is 9-cis-retinoic acid the endogenous ligand for the retinoic acid-X receptor? Nutr Rev. 2006;64:532–8. - PubMed
-
- Germain P, Chambon P, Eichele G, et al. International Union of Pharmacology. LXIII. Retinoid X receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 2006;58:760–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

