The dual EGFR/HER2 inhibitor lapatinib synergistically enhances the antitumor activity of the histone deacetylase inhibitor panobinostat in colorectal cancer models
- PMID: 21464044
- PMCID: PMC3118510
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-2430
The dual EGFR/HER2 inhibitor lapatinib synergistically enhances the antitumor activity of the histone deacetylase inhibitor panobinostat in colorectal cancer models
Abstract
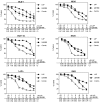
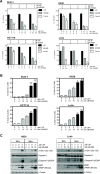
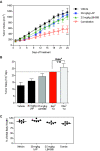
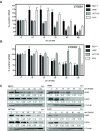
As key molecules that drive progression and chemoresistance in gastrointestinal cancers, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and HER2 have become efficacious drug targets in this setting. Lapatinib is an EGFR/HER2 kinase inhibitor suppressing signaling through the RAS/RAF/MEK (MAP/ERK kinase)/MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) and PI3K (phosphoinositide 3-kinase)/AKT pathways. Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi) are a novel class of agents that induce cell cycle arrest and apoptosis following the acetylation of histone and nonhistone proteins modulating gene expression and disrupting HSP90 function inducing the degradation of EGFR-pathway client proteins. This study sought to evaluate the therapeutic potential of combining lapatinib with the HDACi panobinostat in colorectal cancer (CRC) cell lines with varying EGFR/HER2 expression and KRAS/BRAF/PIK3CA mutations. Lapatinib and panobinostat exerted concentration-dependent antiproliferative effects in vitro (panobinostat range 7.2-30 nmol/L; lapatinib range 7.6-25.8 μmol/L). Combined lapatinib and panobinostat treatment interacted synergistically to inhibit the proliferation and colony formation in all CRC cell lines tested. Combination treatment resulted in rapid induction of apoptosis that coincided with increased DNA double-strand breaks, caspase-8 activation, and PARP cleavage. This was paralleled by decreased signaling through both the PI3K and MAPK pathways and increased downregulation of transcriptional targets including NF-κB1, IRAK1, and CCND1. Panobinostat treatment induced downregulation of EGFR, HER2, and HER3 mRNA and protein through transcriptional and posttranslational mechanisms. In the LoVo KRAS mutant CRC xenograft model, the combination showed greater antitumor activity than either agent alone, with no apparent increase in toxicity. Our results offer preclinical rationale warranting further clinical investigation combining HDACi with EGFR and HER2-targeted therapies for CRC treatment.
©2011 AACR
Figures
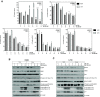
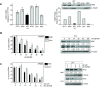
Comment in
-
Revisiting the frontiers of pharmacogenomics of colon cancer.Pharmacogenomics. 2011 Sep;12(9):1243-8. doi: 10.2217/pgs.11.104. Pharmacogenomics. 2011. PMID: 21919602 No abstract available.
References
-
- American Cancer Society . Cancer Facts & Figures 2010. American Cancer Society; Atlanta: 2010.
-
- Giacchetti S, Perpoint B, Zidani R, Le Bail N, Faggiuolo R, Focan C, et al. Phase III multicenter randomized trial of oxaliplatin added to chronomodulated fluorouracil-leucovorin as first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:136–47. - PubMed
-
- Giusti RM, Shastri K, Pilaro AM, Fuchs C, Cordoba-Rodriguez R, Koti K, et al. U.S. Food and Drug Administration approval: panitumumab for epidermal growth factor receptor-expressing metastatic colorectal carcinoma with progression following fluoropyrimidine-, oxaliplatin-, and irinotecan-containing chemotherapy regimens. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:1296–302. - PubMed
-
- Douillard JY, Cunningham D, Roth AD, Navarro M, James RD, Karasek P, et al. Irinotecan combined with fluorouracil compared with fluorouracil alone as first-line treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer: a multicentre randomised trial. Lancet. 2000;355:1041–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

