Differential transformation capacity of Src family kinases during the initiation of prostate cancer
- PMID: 21464326
- PMCID: PMC3080985
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1103904108
Differential transformation capacity of Src family kinases during the initiation of prostate cancer
Abstract
Src family kinases (SFKs) are pleiotropic activators that are responsible for integrating signal transduction for multiple receptors that regulate cellular proliferation, invasion, and metastasis in a variety of human cancers. Independent groups have identified increased expression of individual SFK members during prostate cancer progression, raising the question of whether SFKs display functional equivalence. Here, we show that Src kinase, followed by Fyn kinase and then Lyn kinase, exhibit ranked tumorigenic potential during both paracrine-induced and cell-autonomous-initiated prostate cancer. This quantitative variation in transformation potential appears to be regulated in part by posttranslational palmitoylation. Our data indicate that development of inhibitors against specific SFK members could provide unique targeted therapeutic strategies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

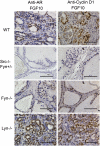



Comment in
-
Re: Differential transformation capacity of Src family kinases during the initiation of prostate cancer.J Urol. 2011 Dec;186(6):2493. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2011.08.048. Epub 2011 Oct 26. J Urol. 2011. PMID: 22078625 No abstract available.
References
-
- Martin GS. The hunting of the Src. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2001;2:467–475. - PubMed
-
- Irby RB, Yeatman TJ. Role of Src expression and activation in human cancer. Oncogene. 2000;19:5636–5642. - PubMed
-
- Orphanos GS, Ioannidis GN, Ardavanis AG. Cardiotoxicity induced by tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Acta Oncol. 2009;48:964–970. - PubMed
-
- Hartmann JT, Haap M, Kopp HG, Lipp HP. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors: A review on pharmacology, metabolism and side effects. Curr Drug Metab. 2009;10:470–481. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

