Phase I dose-escalation study of stereotactic body radiation therapy for low- and intermediate-risk prostate cancer
- PMID: 21464418
- PMCID: PMC3138546
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2010.31.4377
Phase I dose-escalation study of stereotactic body radiation therapy for low- and intermediate-risk prostate cancer
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the tolerability of escalating doses of stereotactic body radiation therapy in the treatment of localized prostate cancer.
Patients and methods: Eligible patients included those with Gleason score 2 to 6 with prostate-specific antigen (PSA) ≤ 20, Gleason score 7 with PSA ≤ 15, ≤ T2b, prostate size ≤ 60 cm(3), and American Urological Association (AUA) score ≤ 15. Pretreatment preparation required an enema and placement of a rectal balloon. Dose-limiting toxicity (DLT) was defined as grade 3 or worse GI/genitourinary (GU) toxicity by Common Terminology Criteria of Adverse Events (version 3). Patients completed quality-of-life questionnaires at defined intervals.
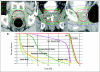
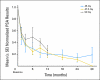
Results: Groups of 15 patients received 45 Gy, 47.5 Gy, and 50 Gy in five fractions (45 total patients). The median follow-up is 30 months (range, 3 to 36 months), 18 months (range, 0 to 30 months), and 12 months (range, 3 to 18 months) for the 45 Gy, 47.5 Gy, and 50 Gy groups, respectively. For all patients, GI grade ≥ 2 and grade ≥ 3 toxicity occurred in 18% and 2%, respectively, and GU grade ≥ 2 and grade ≥ 3 toxicity occurred in 31% and 4%, respectively. Mean AUA scores increased significantly from baseline in the 47.5-Gy dose level (P = .002) as compared with the other dose levels, where mean values returned to baseline. Rectal quality-of-life scores (Expanded Prostate Cancer Index Composite) fell from baseline up to 12 months but trended back at 18 months. In all patients, PSA control is 100% by the nadir + 2 ng/mL failure definition.
Conclusion: Dose escalation to 50 Gy has been completed without DLT. A multicenter phase II trial is underway treating patients to 50 Gy in five fractions to further evaluate this experimental therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures

Comment in
-
Future of treatment for low-risk prostate cancer: for all, for some, or for none?J Clin Oncol. 2011 May 20;29(15):1940-3. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.34.2006. Epub 2011 Apr 4. J Clin Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21464414 No abstract available.
-
[Phase I dose-escalation study of stereotactic body radiation therapy for low- and intermediate-risk prostate cancer].Strahlenther Onkol. 2012 Feb;188(2):192-3. doi: 10.1007/s00066-011-0033-8. Strahlenther Onkol. 2012. PMID: 22218503 German. No abstract available.
References
-
- Timmerman R, Papiez L, McGarry R, et al. Extracranial stereotactic radioablation: Results of a phase I study in medically inoperable stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Chest. 2003;124:1946–1955. - PubMed
-
- Timmerman R, McGarry R, Yiannoutsos C, et al. Excessive toxicity when treating central tumors in a phase II study of stereotactic body radiation therapy for medically inoperable early-stage lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:4833–4839. - PubMed
-
- Schefter TE, Kavanagh BD, Timmerman RD, et al. A phase I trial of stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) for liver metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005;62:1371–1378. - PubMed
-
- Rusthoven KE, Kavanagh BD, Cardenes H, et al. Multi-institutional phase I/II trial of stereotactic body radiation therapy for liver metastases. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:1572–1578. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

