Intracellular leptin-signaling pathways in hypothalamic neurons: the emerging role of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase-phosphodiesterase-3B-cAMP pathway
- PMID: 21464566
- PMCID: PMC3130491
- DOI: 10.1159/000326785
Intracellular leptin-signaling pathways in hypothalamic neurons: the emerging role of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase-phosphodiesterase-3B-cAMP pathway
Abstract
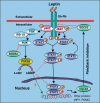
Leptin is secreted primarily by fat cells and acts centrally, particularly in the hypothalamus, to reduce food intake and body weight. Besides the classical JAK2 (Janus kinase-2)-STAT3 (signal transducer and activator of transcription-3) pathway, several non-STAT3 pathways play an important role in mediating leptin signaling in the hypothalamus. We have demonstrated that leptin action in the hypothalamus is mediated by an insulin-like signaling pathway involving stimulation of PI3K (phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase) and PDE3B (phosphodiesterase-3B), and reduction in cAMP levels, and that a PI3K-PDE3B-cAMP pathway interacting with the JAK2-STAT3 pathway constitutes a critical component of leptin signaling in the hypothalamus. It appears that defective regulation of multiple signaling pathways in the hypothalamus causes central leptin resistance, a major cause of obesity. In this regard, we have shown that leptin resistance in hypothalamic neurons following chronic central infusion of this hormone is associated with a defect in the PI3K-PDE3B-cAMP, and not due to compromised signaling in the JAK2-STAT3 pathway. Similarly, the PI3K, but not the STAT3, pathway is impaired in the hypothalamus during the development of diet-induced obesity. Additionally, our recent work suggests that suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 negatively regulates the PI3K pathway of leptin signaling in the hypothalamus, a mechanism expected to play a significant role in diet-induced obesity. Together, the PI3K-PDE3B-cAMP pathway appears to emerge as a major mechanism of leptin signaling in the hypothalamus in regulating energy balance.
Copyright © 2011 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures




References
-
- Zhang Y, Proenca R, Maffei M, Barone M, Leopold L, Friedman JM. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature. 1994;372:425–432. - PubMed
-
- Friedman JM, Halaas JL. Leptin and the regulation of body weight in mammals. Nature. 1998;395:763–770. - PubMed
-
- Sahu A. Leptin signaling in the hypothalamus: emphasis on energy homeostasis and leptin resistance. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2003;24:225–253. - PubMed
-
- Yadav VK, Oury F, Suda N, Liu ZW, Gao XB, Confavreux C, Klemenhagen KC, Tanaka KF, Gingrich JA, Guo XE, Tecott LH, Mann JJ, Hen R, Horvath TL, Karsenty G. A serotonin-dependent mechanism explains the leptin regulation of bone mass, appetite, and energy expenditure. Cell. 2009;138:976–989. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

