miR-9 and let-7g enhance the sensitivity to ionizing radiation by suppression of NFκB1
- PMID: 21464588
- PMCID: PMC3104252
- DOI: 10.3858/emm.2011.43.5.031
miR-9 and let-7g enhance the sensitivity to ionizing radiation by suppression of NFκB1
Abstract
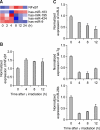
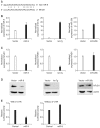
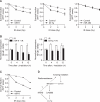
The activation of nuclear factor-kappa B1 (NFkB1) in cancer cells may confer resistance to ionizing radiation (IR). To enhance the therapeutic efficiency of IR in lung cancer, we screened for microRNAs (miRNAs) that suppress NFkB1 and observed their effects on radiosensitivity in a human lung cancer cell line. From time series data of miRNA expression in γ-irradiated H1299 human lung cancer cells, we found that the expression of miR-9 was inversely correlated with that of NFκB1. Overexpression of miR-9 down-regulated the level of NFκB1 in H1299 cells, and the surviving fraction of γ-irradiated cells was decreased. Interestingly, let-7g also suppressed the expression of NFκB1, although there was no canonical target site for let-7g in the NFκB1 3' untranslated region. From these results, we conclude that the expression of miR-9 and let-7g could enhance the efficiency of radiotherapy for lung cancer treatment through the inhibition of NFκB1.
Figures
References
-
- Aggarwal BB, Vijayalekshmi RV, Sung B. Targeting inflammatory pathways for prevention and therapy of cancer: short-term friend, long-term foe. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:425–430. - PubMed
-
- Amundson SA. Functional genomics in radiation biology: a gateway to cellular systems-level studies. Radiat Environ Biophys. 2008;47:25–31. - PubMed
-
- Amundson SA, Bittner M, Fornace AJ., Jr Functional genomics as a window on radiation stress signaling. Oncogene. 2003;22:5828–5833. - PubMed
-
- Chaudhry MA, Kreger B, Omaruddin RA. Transcriptional modulation of micro-RNA in human cells differing in radiation sensitivity. Int J Radiat Biol. 2010;86:569–583. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
