Introduction of the CIITA gene into tumor cells produces exosomes with enhanced anti-tumor effects
- PMID: 21464590
- PMCID: PMC3104250
- DOI: 10.3858/emm.2011.43.5.029
Introduction of the CIITA gene into tumor cells produces exosomes with enhanced anti-tumor effects
Abstract
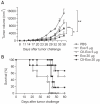
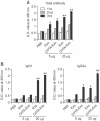
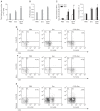
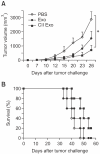
Exosomes are small membrane vesicles secreted from various types of cells. Tumor-derived exosomes contain MHC class I molecules and tumor-specific antigens, receiving attention as a potential cancer vaccine. For induction of efficient anti-tumor immunity, CD4+ helper T cells are required, which recognize appropriate MHC class II-peptide complexes. In this study, we have established an MHC class II molecule-expressing B16F1 murine melanoma cell line (B16F1- CIITA) by transduction of the CIITA (Class II transactivator) gene. Exosomes from B16-CII cells (CIITA- Exo) contained a high amount of MHC class II as well as a tumor antigen TRP2. When loaded on dendritic cells (DCs), CIITA-Exo induced the increased expression of MHC class II molecules and CD86 than the exosomes from the parental cells (Exo). In vitro assays using co-culture of immunized splenocytes and exosome-loaded DCs demonstrated that CIITA-Exo enhanced the splenocyte proliferation and IL-2 secretion. Consistently, compared to B16-Exo, CIITA-Exo induced the increased mRNA levels of inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, chemokine receptor CCR7 and the production of Th1-polarizing cytokine IL-12. A tumor preventive model showed that CIITA-Exo significantly inhibited tumor growth in a dose-dependent manner. Ex vivo assays using immunized mice demonstrated that CIITA-Exo induced a higher amount of Th1-polarized immune responses such as Th1-type IgG2a antibodies and IFN-γ cytokine as well as TRP2-specific CD8+ T cells. A tumor therapeutic model delayed effects of tumor growth by CIITA-Exo. These findings indicate that CIITA-Exo are more efficient as compared to parental Exo to induce anti-tumor immune responses, suggesting a potential role of MHC class II-containing tumor exosomes as an efficient cancer vaccine.
Figures


References
-
- André F, Chaput N, Schartz NE, Flament C, Aubert N, Bernard J, et al. Exosomes as potent cell-free peptide-based vaccine. I. Dendritic cell-derived exosomes transfer functional MHC class I/peptide complexes to dendritic cells. J Immunol. 2004;172:2126–2136. - PubMed
-
- André F, Schartz NE, Chaput N, Flament C, Raposo G, Amigorena S, Angevin E, Zitvogel L. Tumor-derived exosomes: a new source of tumor rejection antigens. Vaccine. 2002;(Suppl 4):A28–A31. - PubMed
-
- Andre F, Schartz NE, Movassagh M, Flament C, Pautier P, Morice P, et al. Malignant effusions and immunogenic tumour-derived exosomes. Lancet. 2002;360:295–305. - PubMed
-
- Baxevanis CN, Voutsas IF, Tsitsilonis OE, Gritzapis AD, Sotiriadou R, Papamichail M. Tumor-specific CD4+ T lymphocytes from cancer patients are required for optimal induction of cytotoxic T cells against the autologous tumor. J Immunol. 2000;164:3902–3912. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
