Expression and roles of Slit/Robo in human ovarian cancer
- PMID: 21465248
- PMCID: PMC3280508
- DOI: 10.1007/s00418-011-0806-2
Expression and roles of Slit/Robo in human ovarian cancer
Abstract
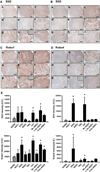
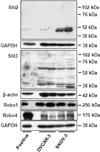
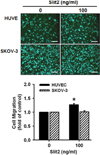
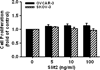
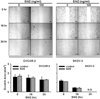
The Slit glycoproteins and their Roundabout (Robo) receptors regulate migration and growth of many types of cells including human cancer cells. However, little is known about the expression and roles of Slit/Robo in human ovarian cancer. Herein, we examined the expression of Slit/Robo in human normal and malignant ovarian tissues and its potential participation in regulating migration and proliferation of human ovarian cancer cells using two ovarian cancer cell lines, OVCAR-3 and SKOV-3. We demonstrated that Slit2/3 and Robo1 were immunolocalized primarily in stromal cells in human normal ovaries and in cancer cells in many histotypes of ovarian cancer tissues. Protein expression of Slit2/3 and Robo1/4 was also identified in OVCAR-3 and SKOV-3 cells. However, recombinant human Slit2 did not significantly affect SKOV-3 cell migration, and OVCAR-3 and SKOV-3 cell proliferation. Slit2 also did not induce ERK1/2 and AKT1 phosphorylation in OVCAR-3 and SKOV-3 cells. The current findings indicate that three major members (Slit2/3 and Robo1) of Slit/Robo family are widely expressed in the human normal and malignant ovarian tissues and in OVCAR-3 and SKOV-3 cells. However, Slit/Robo signaling may not play an important role in regulating human ovarian cancer cell proliferation and migration.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Novel regulated expression of the SLIT/ROBO pathway in the ovary: possible role during luteolysis in women.Endocrinology. 2008 Oct;149(10):5024-34. doi: 10.1210/en.2008-0204. Epub 2008 Jun 19. Endocrinology. 2008. PMID: 18566128
-
Expression of the repulsive SLIT/ROBO pathway in the human endometrium and Fallopian tube.Mol Hum Reprod. 2010 Dec;16(12):950-9. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gaq055. Epub 2010 Jul 22. Mol Hum Reprod. 2010. PMID: 20651036 Free PMC article.
-
Quantification of SLIT-ROBO transcripts in hepatocellular carcinoma reveals two groups of genes with coordinate expression.BMC Cancer. 2008 Dec 29;8:392. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-8-392. BMC Cancer. 2008. PMID: 19114000 Free PMC article.
-
The SLIT/ROBO Pathway in Liver Fibrosis and Cancer.Biomolecules. 2023 May 1;13(5):785. doi: 10.3390/biom13050785. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37238655 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The SLIT-ROBO pathway: a regulator of cell function with implications for the reproductive system.Reproduction. 2010 Apr;139(4):697-704. doi: 10.1530/REP-10-0017. Epub 2010 Jan 25. Reproduction. 2010. PMID: 20100881 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Slit2‑Robo1 signaling promotes the adhesion, invasion and migration of tongue carcinoma cells via upregulating matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9, and downregulating E‑cadherin.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Sep;14(3):1901-6. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5518. Epub 2016 Jul 13. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 27431199 Free PMC article.
-
SLIT2 inhibits cell migration in colorectal cancer through the AKT-GSK3β signaling pathway.Int J Colorectal Dis. 2013 Jul;28(7):933-40. doi: 10.1007/s00384-013-1641-9. Epub 2013 Jan 13. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2013. PMID: 23314850
-
Estradiol 17β and its metabolites stimulate cell proliferation and antagonize ascorbic acid-suppressed cell proliferation in human ovarian cancer cells.Reprod Sci. 2014 Jan;21(1):102-11. doi: 10.1177/1933719113492211. Epub 2013 Jun 11. Reprod Sci. 2014. PMID: 23757313 Free PMC article.
-
Human placental expression of SLIT/ROBO signaling cues: effects of preeclampsia and hypoxia.Biol Reprod. 2012 Apr 12;86(4):111. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.110.088138. Print 2012 Apr. Biol Reprod. 2012. PMID: 22262697 Free PMC article.
-
Recent progress in histochemistry and cell biology.Histochem Cell Biol. 2012 Apr;137(4):403-57. doi: 10.1007/s00418-012-0933-4. Epub 2012 Feb 25. Histochem Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22366957 Review.
References
-
- American Cancer Society at http://www.cancer.org: Cancer Facts & Figures. 2010
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

