Ubiquitin ligase parkin promotes Mdm2-arrestin interaction but inhibits arrestin ubiquitination
- PMID: 21466165
- PMCID: PMC3091828
- DOI: 10.1021/bi200175q
Ubiquitin ligase parkin promotes Mdm2-arrestin interaction but inhibits arrestin ubiquitination
Abstract
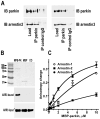
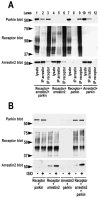
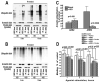
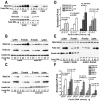
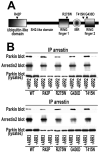
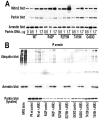
Numerous mutations in E3 ubiquitin ligase parkin were shown to associate with familial Parkinson's disease. Here we show that parkin binds arrestins, versatile regulators of cell signaling. Arrestin-parkin interaction was demonstrated by coimmunoprecipitation of endogenous proteins from brain tissue and shown to be direct using purified proteins. Parkin binding enhances arrestin interactions with another E3 ubiquitin ligase, Mdm2, apparently by shifting arrestin conformational equilibrium to the basal state preferred by Mdm2. Although Mdm2 was reported to ubiquitinate arrestins, parkin-dependent increase in Mdm2 binding dramatically reduces the ubiquitination of both nonvisual arrestins, basal and stimulated by receptor activation, without affecting receptor internalization. Several disease-associated parkin mutations differentially affect the stimulation of Mdm2 binding. All parkin mutants tested effectively suppress arrestin ubiquitination, suggesting that bound parkin shields arrestin lysines targeted by Mdm2. Parkin binding to arrestins along with its effects on arrestin interaction with Mdm2 and ubiquitination is a novel function of this protein with implications for Parkinson's disease pathology.
Figures



References
-
- Kitada T, Asakawa S, Hattori N, Matsumine H, Yamamura Y, Minoshima S, Yokochi M, Mizuno Y, Shimizu N. Mutations in the parkin gene cause autosomal recessive juvenile parkinsonism. Nature. 1998;392:544–545. - PubMed
-
- Lücking CB, Dürr A, Bonifati V, Vaughan J, De Michele G, Gasser T, Harhangi BS, Meco G, Denèfle P, Wood NW, Agid Y, Brice A French Parkinson's Disease Genetics Study Group, and European Consortium on Genetic Susceptibility in Parkinson's Disease. Association between Early-Onset Parkinson's Disease and Mutations in the Parkin Gene. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:1560–1567. - PubMed
-
- Khan NL, Scherfler C, Graham E, Bhatia KP, Quinn N, Lees AJ, Brooks DJ, Wood NW, Piccini P. Dopaminergic dysfunction in unrelated, asymptomatic carriers of a single parkin mutation. Neurology. 2005;64:134–136. - PubMed
-
- Farrer M, Chan P, Chen R, Tan L, Lincoln S, Hernandez D, Forno L, Gwinn-Hardy K, Petrucelli L, Hussey J, Singleton A, Tanner C, Hardy J, Langston W. Lewy bodies and parkinsonism in families with parkin mutations. Ann Neurol. 2001;50:293–300. - PubMed
-
- Pramstaller PP, Scaravilli F, Eskelson C, Pepivani I, Hedrich K, Gonzales-McNeal M, Hilker R, Kramer PL, Klein C. Lewy body Parkinson's disease in a large pedigree with 77 Parkin mutation carriers. Ann Neurol. 2005;58:411–422. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

