Toll-like receptor, RIG-I-like receptors and the NLRP3 inflammasome: key modulators of innate immune responses to double-stranded RNA viruses
- PMID: 21466970
- PMCID: PMC3109132
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2011.02.001
Toll-like receptor, RIG-I-like receptors and the NLRP3 inflammasome: key modulators of innate immune responses to double-stranded RNA viruses
Abstract
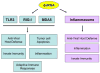
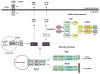
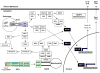
Double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), the genetic material for many RNA viruses, induces robust host immune responses via pattern recognition receptors, which include Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3), retinoic acid-inducible gene-I-like receptors (RLRs) and the multi-protein NLRP3 inflammasome complex. The engagement of dsRNA receptors or inflammasome activation by viral dsRNA initiates complex intracellular signaling cascades that play essential roles in inflammation and innate immune responses, as well as the resultant development of adaptive immunity. This review focuses on signaling pathways mediated by TLR3, RLRs and the NLRP3 inflammasome, as well as the potential use of agonists and antagonists that target these pathways to treat disease.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Akira S, Takeda K. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:499–511. - PubMed
-
- Iwasaki A, Medzhitov R. Toll-like receptor control of the adaptive immune responses. Nat Immunol. 2004;5:987–995. - PubMed
-
- Matsumoto M, Funami K, Tanabe M, et al. Subcellular localization of Toll-like receptor 3 in human dendritic cells. J Immunol. 2003;171:3154–3162. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

