Ric-8B is a GTP-dependent G protein alphas guanine nucleotide exchange factor
- PMID: 21467038
- PMCID: PMC3103368
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.163675
Ric-8B is a GTP-dependent G protein alphas guanine nucleotide exchange factor
Abstract
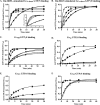
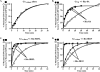
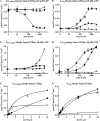
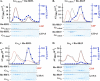
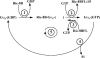
ric-8 (resistance to inhibitors of cholinesterase 8) genes have positive roles in variegated G protein signaling pathways, including Gα(q) and Gα(s) regulation of neurotransmission, Gα(i)-dependent mitotic spindle positioning during (asymmetric) cell division, and Gα(olf)-dependent odorant receptor signaling. Mammalian Ric-8 activities are partitioned between two genes, ric-8A and ric-8B. Ric-8A is a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) for Gα(i)/α(q)/α(12/13) subunits. Ric-8B potentiated G(s) signaling presumably as a Gα(s)-class GEF activator, but no demonstration has shown Ric-8B GEF activity. Here, two Ric-8B isoforms were purified and found to be Gα subunit GDP release factor/GEFs. In HeLa cells, full-length Ric-8B (Ric-8BFL) bound endogenously expressed Gα(s) and lesser amounts of Gα(q) and Gα(13). Ric-8BFL stimulated guanosine 5'-3-O-(thio)triphosphate (GTPγS) binding to these subunits and Gα(olf), whereas the Ric-8BΔ9 isoform stimulated Gα(s short) GTPγS binding only. Michaelis-Menten experiments showed that Ric-8BFL elevated the V(max) of Gα(s) steady state GTP hydrolysis and the apparent K(m) values of GTP binding to Gα(s) from ∼385 nm to an estimated value of ∼42 μM. Directionality of the Ric-8BFL-catalyzed Gα(s) exchange reaction was GTP-dependent. At sub-K(m) GTP, Ric-BFL was inhibitory to exchange despite being a rapid GDP release accelerator. Ric-8BFL binds nucleotide-free Gα(s) tightly, and near-K(m) GTP levels were required to dissociate the Ric-8B·Gα nucleotide-free intermediate to release free Ric-8B and Gα-GTP. Ric-8BFL-catalyzed nucleotide exchange probably proceeds in the forward direction to produce Gα-GTP in cells.
Figures


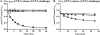
References
-
- Gilman A. G. (1987) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 56, 615–649 - PubMed
-
- Blumer J. B., Chandler L. J., Lanier S. M. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277, 15897–15903 - PubMed
-
- Cismowski M. J. (2006) Semin. Cell. Dev. Biol. 17, 334–344 - PubMed
-
- Natochin M., Campbell T. N., Barren B., Miller L. C., Hameed S., Artemyev N. O., Braun J. E. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280, 30236–30241 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

