Combination radioimmunotherapy and chemoimmunotherapy involving different or the same targets improves therapy of human pancreatic carcinoma xenograft models
- PMID: 21467164
- PMCID: PMC5654622
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0115
Combination radioimmunotherapy and chemoimmunotherapy involving different or the same targets improves therapy of human pancreatic carcinoma xenograft models
Abstract
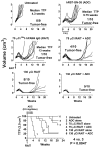
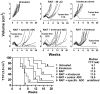
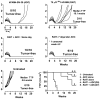
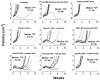
Chemoimmunotherapy with antibody-drug conjugates (ADC) is emerging as a promising therapy for solid tumors, whereas radioimmunotherapy (RAIT) of solid tumors has been relatively ineffective because of their resistance to radiation. We developed antibody-SN-38 conjugates that have significant antitumor activity in xenograft models at nontoxic doses. The goal of this study was to determine if an ADC could be combined with RAIT to enhance efficacy without a commensurate increase in host toxicity. Nude mice bearing human pancreatic cancer xenografts (Capan-1 and BxPC-3) were treated with a single dose of 90Y-labeled antimucin antibody (hPAM4; clivatuzumab tetraxetan) alone or in combination with an anti-Trop-2-SN-38 conjugate, typically administered twice weekly over 4 weeks. The combination, even at RAIT's maximum tolerated dose, controlled tumor progression and cured established xenografts significantly better than the individual treatments without appreciable toxicity. The ADC could be started 1 week after or up to 2 weeks before RAIT with similar enhanced responses, but delaying RAIT for 2 weeks after the ADC was less effective. A nonspecific ADC provided additional benefit over using free drug (irinotecan), but the response was enhanced with the specific ADC. When targeting Capan-1 with ample mucin, hPAM4 could be used as the RAIT and the ADC agent without losing effectiveness, but in BxPC-3 with less mucin, targeting of different antigens was preferred. These studies show the feasibility of combining ADC and RAIT for improved efficacy without increased toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pretargeted radioimmunotherapy of pancreatic cancer xenografts: TF10-90Y-IMP-288 alone and combined with gemcitabine.J Nucl Med. 2009 Dec;50(12):2008-16. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.109.067686. J Nucl Med. 2009. PMID: 19949026
-
Combining radioimmunotherapy and chemotherapy for treatment of medullary thyroid carcinoma: effectiveness of dacarbazine.Cancer. 2002 Jan 1;94(1):51-61. doi: 10.1002/cncr.10157. Cancer. 2002. PMID: 11815960
-
Low-dose radioimmunotherapy ((90)Y-PAM4) combined with gemcitabine for the treatment of experimental pancreatic cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2003 Sep 1;9(10 Pt 2):3929S-37S. Clin Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 14506191
-
New antibody conjugates in cancer therapy.ScientificWorldJournal. 2010 Oct 12;10:2070-89. doi: 10.1100/tsw.2010.191. ScientificWorldJournal. 2010. PMID: 20953556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Phase I trial of 90Y-anti-carcinoembryonic antigen chimeric T84.66 radioimmunotherapy with 5-fluorouracil in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2003 Dec 1;9(16 Pt 1):5842-52. Clin Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 14676105 Review.
Cited by
-
Single-Dose Cisplatin Pre-Treatment Enhances Efficacy of ROBO1-Targeted Radioimmunotherapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 19;21(20):7728. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207728. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33086574 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) associated with the CD20 antigen regulates the rituximab-induced proliferation inhibition in B-cell lymphoma cells.J Biol Chem. 2012 Oct 26;287(44):37109-18. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.404178. Epub 2012 Aug 29. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22932894 Free PMC article.
-
Trial Watch: Tumor-targeting monoclonal antibodies in cancer therapy.Oncoimmunology. 2014 Jan 1;3(1):e27048. doi: 10.4161/onci.27048. Oncoimmunology. 2014. PMID: 24605265 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding the Clinical Impact of MUC5AC Expression on Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jun 19;13(12):3059. doi: 10.3390/cancers13123059. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34205412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiofrequency ablation before intratumoral injection of (131)I-chTNT improves the tumor-to-normal tissue ratio in solid VX2 tumor.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2013 Dec;28(10):725-30. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2012.1418. Epub 2013 Aug 21. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2013. PMID: 23964639 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sharkey RM, Goldenberg DM. Perspectives on cancer therapy with radiolabeled monoclonal antibodies. J Nucl Med. 2005;46(Suppl 1):115S–27S. - PubMed
-
- Hernandez MC, Knox SJ. Radiobiology of radioimmunotherapy with 90Y ibritumomab tiuxetan (Zevalin) Semin Oncol. 2003;30:6–10. - PubMed
-
- Du Y, Honeychurch J, Cragg MS, Bayne M, Glennie MJ, Johnson PW, et al. Antibody-induced intracellular signaling works in combination with radiation to eradicate lymphoma in radioimmunotherapy. Blood. 2004;103:1485–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

