High-quality DNA sequence capture of 524 disease candidate genes
- PMID: 21467225
- PMCID: PMC3080966
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1018981108
High-quality DNA sequence capture of 524 disease candidate genes
Abstract
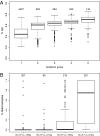
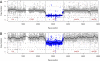
The accurate and complete selection of candidate genomic regions from a DNA sample before sequencing is critical in molecular diagnostics. Several recently developed technologies await substantial improvements in performance, cost, and multiplex sample processing. Here we present the utility of long padlock probes (LPPs) for targeted exon capture followed by array-based sequencing. We found that on average 92% of 5,471 exons from 524 nuclear-encoded mitochondrial genes were successfully amplified from genomic DNA from 63 individuals. Only 144 exons did not amplify in any sample due to high GC content. One LPP was sufficient to capture sequences from <100-500 bp in length and only a single-tube capture reaction and one microarray was required per sample. Our approach was highly reproducible and quick (<8 h) and detected DNA variants at high accuracy (false discovery rate 1%, false negative rate 3%) on the basis of known sample SNPs and Sanger sequence verification. In a patient with clinical and biochemical presentation of ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC) deficiency, we identified copy-number differences in the OTC gene at exon-level resolution. This shows the ability of LPPs to accurately preserve a sample's genome information and provides a cost-effective strategy to identify both single nucleotide changes and structural variants in targeted resequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: S.K., M.N.M., and R.W.D. are named on a patent application for work described in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Albert TJ, et al. Direct selection of human genomic loci by microarray hybridization. Nat Methods. 2007;4:903–905. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

