The association of telomere length and cancer: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 21467229
- PMCID: PMC3111877
- DOI: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-11-0005
The association of telomere length and cancer: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Telomeres shorten with each cell division and are essential for chromosomal stability. Short telomeres in surrogate tissues (e.g., blood cells) are associated with increased cancer risk in several case-control studies, but findings are inconsistent in prospective studies.
Methods: We systematically reviewed studies published prior to August 30, 2010, on the association between telomere length (TL) in surrogate tissues and cancer. There were 27 reports on 13 cancers and/or incident cancer investigating this association. The majority, 16, were retrospective case--control studies, 11 were prospective studies. Meta-analyses were conducted to determine ORs and 95% CIs for these studies.
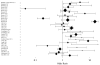
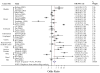
Results: Studies on bladder, esophageal, gastric, head and neck, ovarian, renal, and overall incident cancer found associations between short telomeres and these cancers. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma, breast, lung, and colorectal cancer reports were inconsistent. Single studies on endometrial, prostate, and skin cancers were null. In a random-effects meta-analysis, short TL was significantly associated with cancer in retrospective studies (pooled OR for the shortest TL quartile compared with the longest: 2.9, 95% CI: 1.75-4.8, P < 0.0001). The pooled OR for prospective studies was 1.16 (95% CI: 0.87-1.54, P = 0.32). All studies combined yielded a pooled OR of 1.96 (95% CI: 1.37-2.81, P = 0.0001) for the association of short TL and cancer.
Conclusion and impact: There is suggestive evidence that short surrogate tissue TL is associated with cancer; the strongest evidence exists for bladder, esophageal, gastric, and renal cancers. Additional prospective studies with consistent methodology are needed to confirm this hypothesis.
©2011 AACR.
Figures


References
-
- Palm W, de LT. How shelterin protects mammalian telomeres. Annu Rev Genet. 2008;42:301–34. - PubMed
-
- Aubert G, Lansdorp PM. Telomeres and aging. Physiol Rev. 2008;88(2):557–79. - PubMed
-
- Hornsby PJ. Short telomeres: cause or consequence of aging? Aging Cell. 2006;5(6):577–8. - PubMed
-
- Shawi M, Autexier C. Telomerase, senescence and ageing. Mech Ageing Dev. 2008;129(1-2):3–10. - PubMed
-
- Baird DM. Mechanisms of telomeric instability. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2008;122(3-4):308–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

