Health outcomes after stopping conjugated equine estrogens among postmenopausal women with prior hysterectomy: a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 21467283
- PMCID: PMC3656722
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.2011.382
Health outcomes after stopping conjugated equine estrogens among postmenopausal women with prior hysterectomy: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Context: The Women's Health Initiative Estrogen-Alone Trial was stopped early after a mean of 7.1 years of follow-up because of an increased risk of stroke and little likelihood of altering the balance of risk to benefit by the planned trial termination date. Postintervention health outcomes have not been reported.
Objective: To examine health outcomes associated with randomization to treatment with conjugated equine estrogens (CEE) among women with prior hysterectomy after a mean of 10.7 years of follow-up through August 2009.
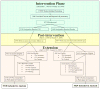
Design, setting, and participants: The intervention phase was a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial of 0.625 mg/d of CEE compared with placebo in 10,739 US postmenopausal women aged 50 to 79 years with prior hysterectomy. Follow-up continued after the planned trial completion date among 7645 surviving participants (78%) who provided written consent.
Main outcome measures: The primary outcomes were coronary heart disease (CHD) and invasive breast cancer. A global index of risks and benefits included these primary outcomes plus stroke, pulmonary embolism, colorectal cancer, hip fracture, and death.
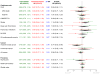
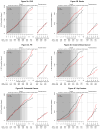
Results: The postintervention risk (annualized rate) for CHD among women assigned to CEE was 0.64% compared with 0.67% in the placebo group (hazard ratio [HR], 0.97; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.75-1.25), 0.26% vs 0.34%, respectively, for breast cancer (HR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.51-1.09), and 1.47% vs 1.48%, respectively, for total mortality (HR, 1.00; 95% CI, 0.84-1.18). The risk of stroke was no longer elevated during the postintervention follow-up period and was 0.36% among women receiving CEE compared with 0.41% in the placebo group (HR, 0.89; 95% CI, 0.64-1.24), the risk of deep vein thrombosis was lower at 0.17% vs 0.27%, respectively (HR, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.41-0.98), and the risk of hip fracture did not differ significantly and was 0.36% vs 0.28%, respectively (HR, 1.27; 95% CI, 0.88-1.82). Over the entire follow-up, lower breast cancer incidence in the CEE group persisted and was 0.27% compared with 0.35% in the placebo group (HR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.62-0.95). Health outcomes were more favorable for younger compared with older women for CHD (P = .05 for interaction), total myocardial infarction (P = .007 for interaction), colorectal cancer (P = .04 for interaction), total mortality (P = .04 for interaction), and global index of chronic diseases (P = .009 for interaction).
Conclusions: Among postmenopausal women with prior hysterectomy followed up for 10.7 years, CEE use for a median of 5.9 years was not associated with an increased or decreased risk of CHD, deep vein thrombosis, stroke, hip fracture, colorectal cancer, or total mortality. A decreased risk of breast cancer persisted.
Trial registration: clinicaltrials.gov Identifier: NCT00000611.
Figures


Comment in
-
Short-term use of unopposed estrogen: a balance of inferred risks and benefits.JAMA. 2011 Apr 6;305(13):1354-5. doi: 10.1001/jama.2011.405. JAMA. 2011. PMID: 21467291 No abstract available.
References
-
- Anderson GL, Limacher M, Assaf AR, et al. Effects of conjugated equine estrogen in postmenopaual women with hysterectomy: the Women’s Health Initiative randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2004;291(14):1701–1712. - PubMed
-
- Women’s Health Initiative Study Group. Design of the Women’s Health Initiative clinical trial and observational study. Control Clin Trials. 1998;19(1):61–109. - PubMed
-
- Curb D, McTiernan A, Heckbert SR, et al. Outcomes ascertainment and adjudication methods in the Women’s Health Initiative. Ann Epidemiol. 2003;13(9 suppl):S122–128. - PubMed
-
- Heiss G, Wallace R, Anderson GL, et al. Health risks and benefits 3 years after stopping randomized treatment with estrogen and progestin. JAMA. 2008;299(9):1036–1045. - PubMed
-
- Cox DR. Regression analysis and life tables. J R Stat Soc. 1972;34:187–220.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- N01WH42119/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 WH042107/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH32106/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH42131/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH42109/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH42114/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 WH032115/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH42115/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 WH032118/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH42111/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH32109/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH42123/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 WH032108/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 WH032119/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH42124/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH32102/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 WH044221/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH42112/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH32122,/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH32112/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH32101/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH42132/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH42121/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH42113/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH42125/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 WH022110/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 WH032100/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 WH032111/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 WH032122/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 WH032118/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH42118/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH32115,/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 WH042107/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH42108/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH32113/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH42120/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH42130/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH42117/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 WH032105/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH42122/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 WH042129/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 WH024152/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH42110/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH42126/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH42116/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

