The MyomiR network in skeletal muscle plasticity
- PMID: 21467943
- PMCID: PMC4871711
- DOI: 10.1097/JES.0b013e31821c01e1
The MyomiR network in skeletal muscle plasticity
Abstract
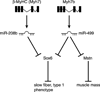
MicroRNA (miRNA) are a class of noncoding RNA involved in regulating gene expression by a posttranscriptional mechanism. Based on work from our laboratory, this review explores the hypothesis that a recently described muscle-specific miRNA, myomiR, network has a central role in the regulation of skeletal muscle plasticity by coordinating changes in fiber type and muscle mass in response to altered contractile activity.
Figures
Comment in
-
Modulation of microRNAs during exercise and disease in human skeletal muscle.Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2011 Oct;39(4):218; author reply 219. doi: 10.1097/JES.0b013e31822ba9e1. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2011. PMID: 21946184 No abstract available.
References
-
- Aoi W, Naito Y, Mizushima K, et al. The microRNA miR-696 regulates PGC-1{alpha} in mouse skeletal muscle in response to physical activity. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010;298:E799–E806. - PubMed
-
- Arasu P, Wightman B, Ruvkun G. Temporal regulation of lin-14 by the antagonistic action of two other heterochronic genes lin-4 and lin-28. Genes Dev. 1991;5:1825–1833. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

