The vasorelaxing effect of hydrogen sulfide on isolated rat aortic rings versus pulmonary artery rings
- PMID: 21468082
- PMCID: PMC4001986
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2011.9
The vasorelaxing effect of hydrogen sulfide on isolated rat aortic rings versus pulmonary artery rings
Abstract
Aim: To compare the vasorelaxing effects of hydrogen sulfide (H(2)S) on isolated aortic and pulmonary artery rings and to determine their action mechanisms.
Methods: H(2)S-induced vasorelaxation of isolated rat aortic versus pulmonary artery rings under 95% O(2) and 5% CO(2) was analyzed. The expression of cystathinonine gamma-lyase (CSE), cystathionine beta synthase (CBS), 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase (3MST), SUR2B and Kir6.1 was examined.
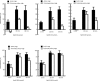
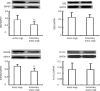
Results: NaHS caused vasorelaxation of rat aortic and pulmonary artery rings in a dose-dependent manner. NaHS dilated aortic rings to a greater extent (16.4%, 38.4%, 64.1%, 84.3%, and 95.9% at concentrations of 50, 100, 200, 500, and 1000 μmol/L, respectively) than pulmonary artery rings (10.1%, 22.2%, 50.6%, 73.6%, and 84.6% at concentrations of 50, 100, 200, 500 and 1000 μmol/L, respectively). The EC(50) of the vasorelaxant effect for aortic rings was 152.17 μmol/L, whereas the EC(50) for pulmonary artery rings was 233.65 μmol/L. The vasorelaxing effect of H(2)S was markedly blocked b y cellular and mitochondrial membrane K(ATP) channel blockers in aortic rings (P<0.01). In contrast, only the cellular membrane K(ATP) channel blocker inhibited H(2)S-induced vasorelaxation in pulmonary artery rings. SUR2B mRNA and protein expression was higher in aortic rings than in pulmonary artery rings. Cystathinonine gamma-lyase (CSE) but not cystathionine beta synthase (CBS) expression in aortic rings was higher than in pulmonary artery rings. 3-Mercapto pyruvate sulfurtransferase (3MST) mRNA was lower in aortic rings than in pulmonary artery rings.
Conclusion: The vasorelaxing effect of H(2)S on isolated aortic rings was more pronounced than the effect on pulmonary artery rings at specific concentrations, which might be associated with increased expression of the K(ATP) channel subunit SUR2B.
Figures




References
-
- Gray GA, Webb DJ. The endothelin system and its potential as a therapeutic target in cardiovascular disease. Pharmacol Ther. 1996;72:109–48. - PubMed
-
- Sata M, Fukuda D. Crucial role of renin-angiotensin system in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. J Med Invest. 2010;57:12–25. - PubMed
-
- Lipworth BJ, Dagg KD. Vasoconstrictor effects of angiotensin II on the pulmonary vascular bed. Chest. 1994;105:1360–4. - PubMed
-
- Olson KR, Dombkowski RA, Russell MJ, Doellman MM, Head SK, Whitfield NL, et al. Hydrogen sulfide as an oxygen sensor/transducer in vertebrate hypoxic vasoconstriction and hypoxic vasodilation. J Exp Biol. 2006;209:4011–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

