Intestinal microbiota and blue baby syndrome: probiotic therapy for term neonates with cyanotic congenital heart disease
- PMID: 21468216
- PMCID: PMC3056099
- DOI: 10.4161/gmic.1.6.14077
Intestinal microbiota and blue baby syndrome: probiotic therapy for term neonates with cyanotic congenital heart disease
Abstract
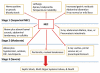
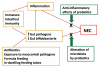
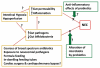
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is the most common intestinal emergency among premature infants. Risk factors in premature infants include immature intestinal immunity and an intestinal microbiota dominated by hospital-acquired bacteria. Some probiotics have been shown to decrease the incidence of NEC in premature infants. Among term infants, NEC is rare. However, among term infants with cyanotic congenital heart disease (CCHD), the incidence of NEC is similar to that of premature infants but with even greater mortality rates. Mechanisms by which NEC occurs in term infants with CCHD are unknown. Of central interest is the potential role of changes in the intestinal microbiota and whether these can be modified with probiotic bacteria; accordingly, we review the literature, propose hypotheses and present the rationale for future studies involving preliminary probiotic clinical trials.
Keywords: bifidobacterium; cyanotic congenital heart disease; intestinal microbiota; necrotizing enterocolitis; probiotic.
© 2010 Landes Bioscience
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bacterial colonization and gut development in preterm neonates.Early Hum Dev. 2012 Mar;88 Suppl 1:S41-9. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2011.12.027. Epub 2012 Jan 28. Early Hum Dev. 2012. PMID: 22284985 Review.
-
Probiotics for the prevention of necrotizing enterocolitis in neonates: an 8-year retrospective cohort study.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2013 Dec;38(6):445-9. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.12084. Epub 2013 Jul 19. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2013. PMID: 23865733
-
Effect of a Dual-Strain Probiotic on Necrotizing Enterocolitis in Neonates with Ductal-Dependent Congenital Heart Disease: A Retrospective Cohort Study.Neonatology. 2020;117(5):569-576. doi: 10.1159/000508831. Epub 2020 Aug 11. Neonatology. 2020. PMID: 32781449
-
Probiotics and the prevention of necrotizing enterocolitis.J Pediatr Surg. 2019 Mar;54(3):405-412. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2018.08.055. Epub 2018 Sep 6. J Pediatr Surg. 2019. PMID: 30241961 Review.
-
Prevention of Necrotizing Enterocolitis Through Manipulation of the Intestinal Microbiota of the Premature Infant.Clin Ther. 2016 Apr;38(4):716-32. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2016.01.006. Epub 2016 Feb 9. Clin Ther. 2016. PMID: 26872618 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Intestinal microbiome changes in an infant with right atrial isomerism and recurrent necrotizing enterocolitis: A case report and review of literature.World J Clin Cases. 2022 Oct 16;10(29):10583-10599. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i29.10583. World J Clin Cases. 2022. PMID: 36312470 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Impact of a Pregnant Woman's Microbiota on the Development of Fetal Heart Defects: A Review of the Literature.Biomedicines. 2024 Mar 14;12(3):654. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12030654. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38540267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Particular genomic and virulence traits associated with preterm infant-derived toxigenic Clostridium perfringens strains.Nat Microbiol. 2023 Jun;8(6):1160-1175. doi: 10.1038/s41564-023-01385-z. Epub 2023 May 25. Nat Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37231089 Free PMC article.
-
Analyzing the Complicated Connection Between Intestinal Microbiota and Cardiovascular Diseases.Cureus. 2022 Aug 19;14(8):e28165. doi: 10.7759/cureus.28165. eCollection 2022 Aug. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36148181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A pilot study of Bifidobacterium breve in neonates undergoing surgery for congenital heart disease.J Intensive Care. 2014 Jun 5;2:36. doi: 10.1186/2052-0492-2-36. eCollection 2014. J Intensive Care. 2014. PMID: 25960878 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blalock A, Taussig HB. Landmark article May 19, 1945: The surgical treatment of malformations of the heart in which there is pulmonary stenosis or pulmonary atresia. JAMA. 1984;27(251):2123–2138. By Blalock A, Taussig HB. - PubMed
-
- Pigula FA, Khalil PN, Mayer JE, del Nido PJ, Jonas RA. Repair of tetralogy of Fallot in neonates and young infants. Circulation. 1999;100:157–161. - PubMed
-
- Murphy AM, Cameron DE. The Blalock-Taussig-Thomas collaboration: a model for medical progress. JAMA. 2008;300:328–330. - PubMed
-
- Williams JA, Bansal AK, Kim BJ, Nwakanma LU, Patel ND, Seth AK, et al. Two thousand Blalock-Taussig shunts: a six-decade experience. Ann Thorac Surg. 2007;84:2070–2075. - PubMed
-
- Lin PW, Nasr TR, Stoll BJ. Necrotizing enterocolitis: recent scientific advances in pathophysiology and prevention. Semin Perinatol. 2008;32:70–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
