Time-related changes in detrusor overactivity in awake rats with spinal cord injury observed by simultaneous registrations of intravesical and intraabdominal pressures
- PMID: 21468282
- PMCID: PMC3070220
- DOI: 10.5213/inj.2011.15.1.19
Time-related changes in detrusor overactivity in awake rats with spinal cord injury observed by simultaneous registrations of intravesical and intraabdominal pressures
Abstract
Purpose: To compare the physical characteristics of detrusor overactivity (DO) induced by intravesical infusion of saline in awake, sham rats and rats with chronic spinal cord injury (SCI), by simultaneous registrations of intravesical and intraabdominal pressures.
Methods: Male Sprague-Dawley rats, normal or with a spinal vascular clip at the level of Th9, were investigated cystometrically 1 and 4 weeks after SCI. Intravesical pressure (IVP) and intraabdominal pressure (IAP) were recorded simultaneously to evaluate true DO. During the filling phase, the event of IVP rises, defined as increments that exceeded 2 cmH(2)O from baseline, were determined as DO according to the absence of simultaneous changes in IAP.
Results: All SCI rats exhibited DO during the filling phase, which was not shown in sham rats. The frequency and pressure of DO had a tendency to decrease with time. The DO frequency of SCI rats after 4 weeks (0.9±0.2 min(-1)) was decreased compared with that after 1 week (2.1±0.4 min(-1); P<0.05). The DO pressure of SCI rats after 4 weeks (8.4±1.9 cmH(2)O) was decreased compared with that after 1 week (11.6±2.9 cmH(2)O; P>0.05).
Conclusions: Cystometric studies in awake male SCI rats showed some significant changes in bladder function after SCI. All SCI rats exhibited DO during the filling phase, and showed different physical characteristics of DO over the course of time. The neurological basis of these time-related changes remains poorly understood, but may provide important prognostic information about long-term urological management in SCI patients.
Keywords: Overactive detrusor; Spinal cord injuries; Urodynamics.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
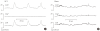
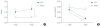


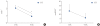
Similar articles
-
Intravesical PGE2 Administration in Conscious Rats as an Experimental Model of Detrusor Overactivity Observed by Simultaneous Registrations of Intravesical and Intraabdominal Pressures.Int Neurourol J. 2010 Aug;14(2):69-77. doi: 10.5213/inj.2010.14.2.69. Epub 2010 Aug 31. Int Neurourol J. 2010. PMID: 21120215 Free PMC article.
-
Urodynamic findings in an awake chemical cystitis rat model observed by simultaneous registrations of intravesical and intraabdominal pressures.Int Neurourol J. 2010 Apr;14(1):54-60. doi: 10.5213/inj.2010.14.1.54. Epub 2010 Apr 30. Int Neurourol J. 2010. PMID: 21120177 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous registration of intraabdominal and intravesical pressures during cystometry in conscious rats--effects of bladder outlet obstruction and intravesical PGE2.Neurourol Urodyn. 2008;27(1):88-95. doi: 10.1002/nau.20460. Neurourol Urodyn. 2008. PMID: 17565725
-
Development and changes with age of detrusor overactivity in spontaneous hypertensive rats as observed by simultaneous registrations of intravesical and intraabdominal pressures.Int Neurourol J. 2011 Dec;15(4):192-8. doi: 10.5213/inj.2011.15.4.192. Epub 2011 Dec 31. Int Neurourol J. 2011. PMID: 22259732 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-analysis of botulinum toxin A detrusor injections in the treatment of neurogenic detrusor overactivity after spinal cord injury.Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2013 Aug;94(8):1473-81. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2013.04.011. Epub 2013 Apr 28. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2013. PMID: 23632286 Review.
Cited by
-
Nonselective blocking of the sympathetic nervous system decreases detrusor overactivity in spontaneously hypertensive rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(4):5048-5059. doi: 10.3390/ijms13045048. Epub 2012 Apr 23. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22606029 Free PMC article.
-
Flow Starting Point and Voiding Mechanisms Measured by Simultaneous Registrations of Intravesical, Intra-abdominal, and Intraurethral Pressures in Awake Rats.Int Neurourol J. 2014 Jun;18(2):68-76. doi: 10.5213/inj.2014.18.2.68. Epub 2014 Jun 26. Int Neurourol J. 2014. PMID: 24987559 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yoshiyama M, Nezu FM, Yokoyama O, Chancellor MB, de Groat WC. Influence of glutamate receptor antagonists on micturition in rats with spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol. 1999;159:250–257. - PubMed
-
- de Sèze M, Wiart L, de Sèze MP, Soyeur L, Dosque JP, Blajezewski S, et al. Intravesical capsaicin versus resiniferatoxin for the treatment of detrusor hyperreflexia in spinal cord injured patients: a double-blind, randomized, controlled study. J Urol. 2004;171:251–255. - PubMed
-
- Elliott S, Krassioukov A. Malignant autonomic dysreflexia in spinal cord injured men. Spinal Cord. 2006;44:386–392. - PubMed
-
- de Groat WC, Kawatani M, Hisamitsu T, Cheng CL, Ma CP, Thor K, et al. Mechanisms underlying the recovery of urinary bladder function following spinal cord injury. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1990;30(Suppl):S71–S77. - PubMed
-
- Jonas U, Jones LW, Tanagho EA. Recovery of bladder function after spinal cord transection. J Urol. 1975;113:626–628. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

