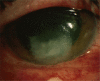
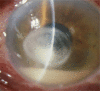
Fungal keratitis
- PMID: 21468333
- PMCID: PMC3065567
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S10819
Fungal keratitis
Abstract
Clinical question: What is the most appropriate management of fungal keratitis?
Results: Traditionally, topical Natamycin is the most commonly used medication for filamentous fungi while Amphotericin B is most commonly used for yeast. Voriconazole is rapidly becoming the drug of choice for all fungal keratitis because of its wide spectrum of coverage and increased penetration into the cornea.
Implementation: Repeated debridement of the ulcer is recommended for the penetration of topical medications. While small, peripheral ulcers may be treated in the community, larger or central ulcers, especially if associated with signs suggestive of anterior chamber penetration should be referred to a tertiary center. Prolonged therapy for approximately four weeks is usually necessary.
Keywords: antifungal medications; debridement; fungal keratitis; keratomycosis.
Figures
References
-
- Liesegang TJ, Forster RK. Spectrum of microbial keratitis in South Florida. Am J Ophthalmol. 1980;90:38–47. - PubMed
-
- Iyer SA, Tuli SS, Wagoner RC. Fungal keratitis: emerging trends and treatment outcomes. Eye Contact Lens. 2006;32:267–271. - PubMed
-
- Gower EW, Keay LJ, Oechsler RA, et al. Trends in fungal keratitis in the United States, 2001 to 2007. Ophthalmology. 2010;117:2263–2267. - PubMed
-
- Gopinathan U, Garg P, Fernandes M, Sharma S, Athmanathan S, Rao GN. The epidemiological features and laboratory results of fungal keratitis: a 10-year review at a referral eye care center in South India. Cornea. 2002;21:555–559. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources