Anti-nociceptive effect of kinin B₁ and B₂ receptor antagonists on peripheral neuropathy induced by paclitaxel in mice
- PMID: 21470206
- PMCID: PMC3188922
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01408.x
Anti-nociceptive effect of kinin B₁ and B₂ receptor antagonists on peripheral neuropathy induced by paclitaxel in mice
Abstract
Background and purpose: In the current study, we investigated the role of both kinin B₁ and B₂ receptors in peripheral neuropathy induced by the chronic treatment of mice with paclitaxel a widely used chemotherapeutic agent.
Experimental approach: Chemotherapy-evoked hyperalgesia was induced by i.p. injections of paclitaxel (2 mg·kg⁻¹) over 5 consecutive days. Mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia were evaluated between 7 and 21 days after the first paclitaxel treatment.
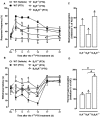
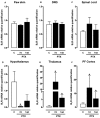
Key results: Treatment with paclitaxel increased both mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia in mice (C57BL/6 and CD1 strains). Kinin receptor deficient mice (B₁, or B₂ receptor knock-out and B₁B₂ receptor, double knock-out) presented a significant reduction in paclitaxel-induced hypernociceptive responses in comparison to wild-type animals. Treatment of CD1 mice with kinin receptor antagonists (DALBK for B₁ or Hoe 140 for B₂ receptors) significantly inhibited both mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia when tested at 7 and 14 days after the first paclitaxel injection. DALBK and Hoe 140 were also effective against paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy when given intrathecally or i.c.v. A marked increase in B₁ receptor mRNA was observed in the mouse thalamus, parietal and pre-frontal cortex from 7 days after the first paclitaxel treatment.
Conclusions and implications: Kinins acting on both B₁ and B₂ receptors, expressed in spinal and supra-spinal sites, played a crucial role in controlling the hypernociceptive state caused by chronic treatment with paclitaxel.
© 2011 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2011 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
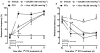



Similar articles
-
Kinin Receptors Sensitize TRPV4 Channel and Induce Mechanical Hyperalgesia: Relevance to Paclitaxel-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Mice.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Mar;55(3):2150-2161. doi: 10.1007/s12035-017-0475-9. Epub 2017 Mar 10. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 28283888
-
The role of kinin B1 and B2 receptors in the scratching behaviour induced by proteinase-activated receptor-2 agonists in mice.Br J Pharmacol. 2010 Feb;159(4):888-97. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00571.x. Epub 2010 Jan 8. Br J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20067469 Free PMC article.
-
The use of kinin B1 and B2 receptor knockout mice and selective antagonists to characterize the nociceptive responses caused by kinins at the spinal level.Neuropharmacology. 2002 Dec;43(7):1188-97. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(02)00311-8. Neuropharmacology. 2002. PMID: 12504926
-
The kallikrein-kinin system: current and future pharmacological targets.J Pharmacol Sci. 2005 Sep;99(1):6-38. doi: 10.1254/jphs.srj05001x. J Pharmacol Sci. 2005. PMID: 16177542 Review.
-
Kinin B1 receptors as a therapeutic target for inflammation.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2018 Jan;22(1):31-44. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2018.1409724. Epub 2017 Nov 30. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2018. PMID: 29168929 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanism-based treatment for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathic pain.Nat Rev Neurol. 2014 Dec;10(12):694-707. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2014.211. Epub 2014 Nov 4. Nat Rev Neurol. 2014. PMID: 25366108 Review.
-
Kinin B2 and B1 Receptors Activation Sensitize the TRPA1 Channel Contributing to Anastrozole-Induced Pain Symptoms.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Apr 3;15(4):1136. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15041136. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37111622 Free PMC article.
-
Review of the Role of the Brain in Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Jun 11;8:693133. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.693133. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34179101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kinin B1 and B2 Receptors Contribute to Cisplatin-Induced Painful Peripheral Neuropathy in Male Mice.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Mar 6;15(3):852. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15030852. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36986713 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic, Intrathecal, and Intracerebroventricular Antihyperalgesic Effects of the Calcium Channel Blocker CTK 01512-2 Toxin in Persistent Pain Models.Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Jul;59(7):4436-4452. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-02864-w. Epub 2022 May 16. Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 35570263
References
-
- Alfie ME, Sigmon DH, Pomposiello SI, Carretero OA. Effect of high salt intake in mutant mice lacking bradykinin-B2 receptors. Hypertension. 1997;29:483–487. - PubMed
-
- Alfie ME, Alim S, Mehta D, Shesely EG, Carretero OA. An enhanced effect of arginine vasopressin in bradykinin B2 receptor null mutant mice. Hypertension. 1999;33:1436–1440. - PubMed
-
- Begley DJ, Brightman MW. Structural and functional aspects of the blood–brain barrier. Prog Drug Res. 2003;61:39–78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

