Glucosidase II and N-glycan mannose content regulate the half-lives of monoglucosylated species in vivo
- PMID: 21471007
- PMCID: PMC3103398
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E11-01-0019
Glucosidase II and N-glycan mannose content regulate the half-lives of monoglucosylated species in vivo
Abstract
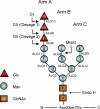
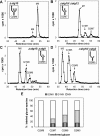
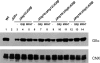
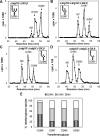
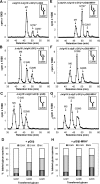
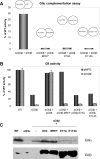
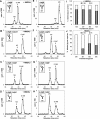
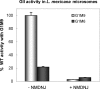
Glucosidase II (GII) sequentially removes the two innermost glucose residues from the glycan (Glc(3)Man(9)GlcNAc(2)) transferred to proteins. GII also participates in cycles involving the lectin/chaperones calnexin (CNX) and calreticulin (CRT) as it removes the single glucose unit added to folding intermediates and misfolded glycoproteins by the UDP-Glc:glycoprotein glucosyltransferase (UGGT). GII is a heterodimer in which the α subunit (GIIα) bears the active site, and the β subunit (GIIβ) modulates GIIα activity through its C-terminal mannose 6-phosphate receptor homologous (MRH) domain. Here we report that, as already described in cell-free assays, in live Schizosaccharomyces pombe cells a decrease in the number of mannoses in the glycan results in decreased GII activity. Contrary to previously reported cell-free experiments, however, no such effect was observed in vivo for UGGT. We propose that endoplasmic reticulum α-mannosidase-mediated N-glycan demannosylation of misfolded/slow-folding glycoproteins may favor their interaction with the lectin/chaperone CNX present in S. pombe by prolonging the half-lives of the monoglucosylated glycans (S. pombe lacks CRT). Moreover, we show that even N-glycans bearing five mannoses may interact in vivo with the GIIβ MRH domain and that the N-terminal GIIβ G2B domain is involved in the GIIα-GIIβ interaction. Finally, we report that protists that transfer glycans with low mannose content to proteins have nevertheless conserved the possibility of displaying relatively long-lived monoglucosylated glycans by expressing GIIβ MRH domains with a higher specificity for glycans with high mannose content.
Figures
References
-
- Alfa C, Fantes P, Hyams J, McLeod M, Wabrik E. Experiments with Fission Yeast: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1993.
-
- Arendt CW, Ostergaard HL. Two distinct domains of the β subunit of glucosidase II interact with the catalytic α-subunit. Glycobiology. 2000;10:487–492. - PubMed
-
- Bähler J, Wu JQ, Longtine MS, Shah NG, McKenzie A 3rd, Steever AB, Wach A, Philippsen P, Pringle JR. Heterologous modules for efficient and versatile PCR-based gene targeting in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Yeast. 1998;14:943–951. - PubMed
-
- Cabral CM, Liu Y, Sifers RN. Dissecting glycoprotein quality control in the secretory pathway. Trends Biochem Sci. 2001;26:619–624. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

