Apolipoprotein E regulates the integrity of tight junctions in an isoform-dependent manner in an in vitro blood-brain barrier model
- PMID: 21471207
- PMCID: PMC3093828
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.225532
Apolipoprotein E regulates the integrity of tight junctions in an isoform-dependent manner in an in vitro blood-brain barrier model
Abstract
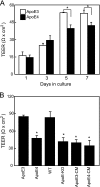
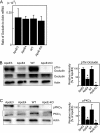
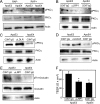
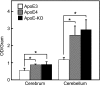
Apolipoprotein E (apoE) is a major apolipoprotein in the brain. The ε4 allele of apoE is a major risk factor for Alzheimer disease, and apoE deficiency in mice leads to blood-brain barrier (BBB) leakage. However, the effect of apoE isoforms on BBB properties are as yet unknown. Here, using an in vitro BBB model consisting of brain endothelial cells and pericytes prepared from wild-type (WT) mice, and primary astrocytes prepared from human apoE3- and apoE4-knock-in mice, we show that the barrier function of tight junctions (TJs) was impaired when the BBB was reconstituted with primary astrocytes from apoE4-knock-in mice (apoE4-BBB model). The phosphorylation of occludin at Thr residues and the activation of protein kinase C (PKC)η in mBECs were attenuated in the apoE4-BBB model compared with those in the apoE3-BBB model. The differential effects of apoE isoforms on the activation of PKCη, the phosphorylation of occludin at Thr residues, and TJ integrity were abolished following the treatment with an anti-low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (LRP1) antibody or a LRP1 antagonist receptor-associated protein. Consistent with the results of in vitro studies, BBB permeability was higher in apoE4-knock-in mice than in apoE3-knock-in mice. Our studies provide evidence that TJ integrity in BBB is regulated by apoE in an isoform-dependent manner.
© 2011 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
apoE isoform-specific disruption of amyloid beta peptide clearance from mouse brain.J Clin Invest. 2008 Dec;118(12):4002-13. doi: 10.1172/JCI36663. Epub 2008 Nov 13. J Clin Invest. 2008. PMID: 19033669 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein E4 impairs spontaneous blood brain barrier repair following traumatic brain injury.Mol Neurodegener. 2018 Apr 4;13(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s13024-018-0249-5. Mol Neurodegener. 2018. PMID: 29618365 Free PMC article.
-
Blood-brain barrier-associated pericytes internalize and clear aggregated amyloid-β42 by LRP1-dependent apolipoprotein E isoform-specific mechanism.Mol Neurodegener. 2018 Oct 19;13(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s13024-018-0286-0. Mol Neurodegener. 2018. PMID: 30340601 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein E and oxidative stress in brain with relevance to Alzheimer's disease.Neurobiol Dis. 2020 May;138:104795. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2020.104795. Epub 2020 Feb 6. Neurobiol Dis. 2020. PMID: 32036033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An apolipoprotein E receptor mimetic peptide decreases blood-brain barrier permeability following intracerebral hemorrhage by inhibiting the CypA/MMP-9 signaling pathway via LRP1 activation.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Dec 25;143(Pt 3):113007. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113007. Epub 2024 Oct 31. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39486173 Review.
Cited by
-
ApoE4 induces Aβ42, tau, and neuronal pathology in the hippocampus of young targeted replacement apoE4 mice.Mol Neurodegener. 2013 May 17;8:16. doi: 10.1186/1750-1326-8-16. Mol Neurodegener. 2013. PMID: 23684315 Free PMC article.
-
Role of membrane biophysics in Alzheimer's-related cell pathways.Front Neurosci. 2015 May 27;9:186. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2015.00186. eCollection 2015. Front Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26074758 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelial Dysfunction in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 2;24(3):2909. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032909. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36769234 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alzheimer's Disease: An Update and Insights Into Pathophysiology.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Mar 30;14:742408. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.742408. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35431894 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ApoE and Aβ in Alzheimer's disease: accidental encounters or partners?Neuron. 2014 Feb 19;81(4):740-54. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.01.045. Neuron. 2014. PMID: 24559670 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mahley R. W. (1988) Science 240, 622–630 - PubMed
-
- Corder E. H., Saunders A. M., Strittmatter W. J., Schmechel D. E., Gaskell P. C., Small G. W., Roses A. D., Haines J. L., Pericak-Vance M. A. (1993) Science 261, 921–923 - PubMed
-
- Saunders A. M., Strittmatter W. J., Schmechel D., George-Hyslop P. H., Pericak-Vance M. A., Joo S. H., Rosi B. L., Gusella J. F., Crapper-MacLachlan D. R., Alberts M. J., et al. (1993) Neurology 43, 1467–1472 - PubMed
-
- Herz J., Bock H. H. (2002) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 71, 405–434 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

