Rapid differentiation of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus by flow cytometry after brief antibiotic exposure
- PMID: 21471343
- PMCID: PMC3122745
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.02548-10
Rapid differentiation of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus by flow cytometry after brief antibiotic exposure
Abstract
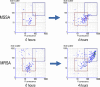
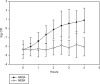
We noticed that methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and methicillin-susceptible S. aureus (MSSA) isolates yielded side-scatter (SSC) and fluorescence intensity (FI) differences on flow cytometry (FCM) following incubation in oxacillin broth. The purpose of this study was to determine whether MRSA and MSSA could be reliably differentiated by FCM. S. aureus isolates were incubated in oxacillin-containing Mueller-Hinton broth, stained using the FASTEST total viable organisms kit, and analyzed by FCM in the MicroPRO instrument. SSC versus FI were examined, and gates 1 and 2 were defined to encompass the majority of MSSA and MRSA signal events, respectively. A count ratio (CR) was defined as the ratio of counts in gate 2 to those in gate 1. Initially, 33 isolates were tested after 4 h of incubation for proof-of-concept. Twenty others were then tested after incubation intervals ranging from 30 min to 4 h to determine the earliest possible time for differentiation. Next, 100 separate isolates were tested to determine the best CR cutoff value. Finally, the CR was validated by using an independent cohort of 121 isolates. We noted that MRSA isolates had higher SSC and FI readings than did MSSA isolates after 2 h of incubation. The receiver-operator characteristics curve showed that a CR cutoff of 0.0445 reliably differentiated MRSA from MSSA. In the validation cohort, this cutoff had a sensitivity of 100% and a specificity of 98.7% for identifying MRSA from among S. aureus isolates, following 2 h of incubation. This study demonstrates that MRSA and MSSA can be accurately differentiated by FCM after 2 h of incubation in an oxacillin-containing liquid culture medium.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

