Physiological identification and infralimbic responsiveness of rat intercalated amygdala neurons
- PMID: 21471396
- PMCID: PMC3118749
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00136.2011
Physiological identification and infralimbic responsiveness of rat intercalated amygdala neurons
Abstract
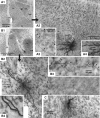
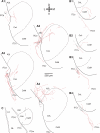
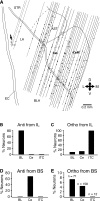
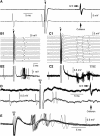
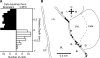
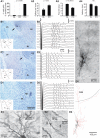
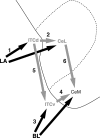
Intercalated (ITC) amygdala neurons are thought to play a critical role in the extinction of conditioned fear. However, several factors hinder progress in studying ITC contributions to extinction. First, although extinction is usually studied in rats and mice, most ITC investigations were performed in guinea pigs or cats. Thus it is unclear whether their connectivity is similar across species. Second, we lack criteria to identify ITC cells on the basis of their discharge pattern. As a result, key predictions of ITC extinction models remain untested. Among these, ITC cells were predicted to be strongly excited by infralimbic inputs, explaining why infralimbic inhibition interferes with extinction. To study the connectivity of ITC cells, we labeled them with neurobiotin during patch recordings in slices of the rat amygdala. This revealed that medially located ITC cells project topographically to the central nucleus and to other ITC clusters located more ventrally. To study the infralimbic responsiveness of ITC cells, we performed juxtacellular recording and labeling of amygdala cells with neurobiotin in anesthetized rats. All ITC cells were orthodromically responsive to infralimbic stimuli, and their responses usually consisted of high-frequency (~350 Hz) trains of four to six spikes, a response pattern never seen in neighboring amygdala nuclei. Overall, our results suggest that the connectivity of ITC cells is conserved across species and that ITC cells are strongly responsive to infralimbic stimuli, as predicted by extinction models. The unique response pattern of ITC cells to infralimbic stimuli can now be used to identify them in fear conditioning experiments.
Figures


References
-
- Blechert J, Michael T, Vriends N, Margraf J, Wilhelm FH. Fear conditioning in posttraumatic stress disorder: evidence for delayed extinction of autonomic, experiential, and behavioural responses. Behav Res Ther 45: 2019–2033, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Cassell MD, Wright DJ. Topography of projections from the medial prefrontal cortex to the amygdala in the rat. Brain Res Bull 17: 321–333, 1986 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

