AAV-mediated in vivo knockdown of luciferase using combinatorial RNAi and U1i
- PMID: 21472008
- PMCID: PMC3169806
- DOI: 10.1038/gt.2011.41
AAV-mediated in vivo knockdown of luciferase using combinatorial RNAi and U1i
Abstract
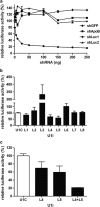
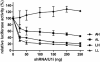
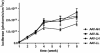
RNA interference (RNAi) has been successfully employed for specific inhibition of gene expression; however, safety and delivery of RNAi remain critical issues. We investigated the combinatorial use of RNAi and U1 interference (U1i). U1i is a gene-silencing technique that acts on the pre-mRNA by preventing polyadenylation. RNAi and U1i have distinct mechanisms of action in different cellular compartments and their combined effect allows usage of minimal doses, thereby avoiding toxicity while retaining high target inhibition. As a proof of concept, we investigated knockdown of the firefly luciferase reporter gene by combinatorial use of RNAi and U1i, and evaluated their inhibitory potential both in vitro and in vivo. Co-transfection of RNAi and U1i constructs showed additive reduction of luciferase expression up to 95% in vitro. We attained similar knockdown when RNAi and U1i constructs were hydrodynamically transfected into murine liver, demonstrating for the first time successful in vivo application of U1i. Moreover, we demonstrated long-term gene silencing by AAV-mediated transduction of murine muscle with RNAi/U1i constructs targeting firefly luciferase. In conclusion, these results provide a proof of principle for the combinatorial use of RNAi and U1i to enhance target gene knockdown in vivo.
Figures
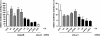

References
-
- Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA, Driver SE, Mello CC. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1998;391:806–811. - PubMed
-
- Meister G, Tuschl T. Mechanisms of gene silencing by double-stranded RNA. Nature. 2004;431:343–349. - PubMed
-
- Zamore PD, Tuschl T, Sharp PA, Bartel DP. RNAi: Double-stranded RNA directs the ATP-dependent cleavage of mRNA at 21–23 nucleotide intervals. Cell. 2000;101:25–33. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

